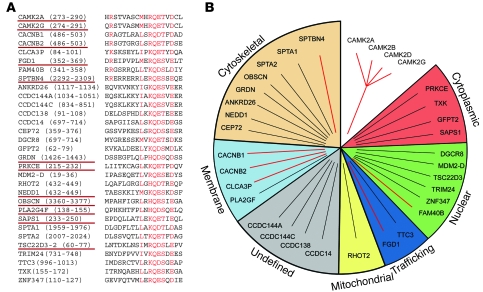
Figure 1. Identification of putative new CaMKII-binding proteins.
(A) Putative CaMKII-targeting proteins identified through a screen of the human genome using a sequence from the CaMKII autoregulatory domain as bait. Candidates with the highest homology to CaMKII autoregulatory domain are listed first. (B) Candidate targeting molecules included cytoskeletal, nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitochondrial proteins with identified roles in cell metabolism, cytoskeletal dynamics, and signaling. All CaMKII gene products (α, β, γ, and δ) were recognized by the screen; notably, only 1 known CaMKII-binding partner was identified (β2a). Candidates were cloned from human cDNA, and CaMKII-binding activity was assessed by in vitro binding assays using radiolabeled target proteins and activated CaMKII (CaMKII T287D). Notably, only clones underlined in red in A showed robust binding for CaMKII.