Figure 8.
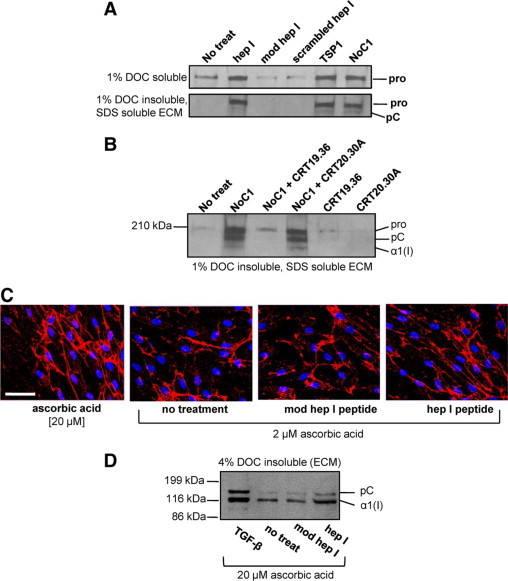
TSP1 binding to CRT increases collagen deposition into the insoluble extracellular matrix fraction of fibroblasts. A: MEFs were treated daily for three days in media with 0.5% FBS, 2 μmol/L ascorbic acid, and with 10 μmol/L hep I, 10 μmol/L modified hep I, 10 μmol/L scrambled hep I, 67 nmol/L TSP1, or 30 nmol/L NoC1. Cellular and pericellular protein was harvested with 1% DOC extraction (top), and the DOC-insoluble ECM was harvested with 2× SDS Laemmli buffer (bottom), separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes for immunoblotting with rabbit anti-mouse collagen I. Pro indicates procollagen; pC, procollagen with N-terminal propeptide removed, α1 (I), collagen I with both C- and N-terminal propeptides removed. B: MEFs were treated daily for three days as described above and with 30 nmol/L NoC1 in the presence or absence of 25-fold molar excess of CRT19.36 or control CRT20.30A peptide (750 nmol/L). The 1% DOC insoluble, SDS-soluble ECM was harvested, separated by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted for type I collagen. C: Type I collagen fibril formation in human foreskin fibroblasts was detected by immunofluorescence with rabbit anti-collagen I antibody and a Texas Red-labeled secondary antibody (red). Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Cells were treated daily for three days in the presence of 20 μmol/L ascorbic acid with no additional treatment or in the presence of 2 μmol/L ascorbic acid with either 5 μmol/L hep I peptide, 5 μmol/L modified hep I peptide, or media only. Scale bar = 60 μm. D: Human foreskin fibroblasts were treated daily for three days in FGM containing 0.5% FBS, 20 μmol/L ascorbic acid, and 5 μmol/L hep I peptide, 5 μmol/L modified hep I peptide, or 10 pmol/L TGF-β1. Cell matrices were separated by extraction in 4% DOC, and DOC-insoluble ECM was separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes for immunoblotting with rabbit anti-human collagen I. Bands were labeled as described above.
