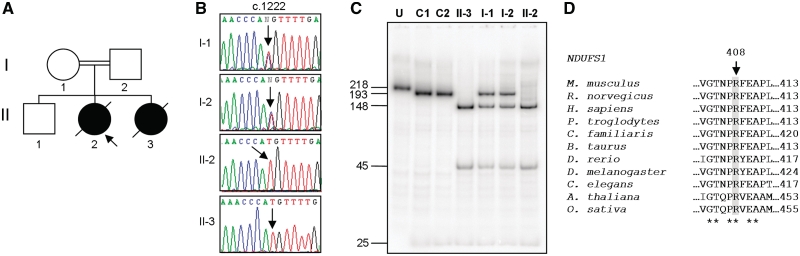
Figure 2.
NDUFS1 homozygous mutation, c.1222C>T (p.R408C). (A) Family 5 pedigree, (B) sequence electropherograms of NDUFS1 gene with c.1222 position highlighted in patient and family members, (C) confirmation of homozygous c.1222C>T mutation by PCR–RFLP. U = uncut; C1 = Control 1; C2 = Control 2. RFLP products were separated through a 12% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The wild-type PCR product contains a single NlaIII site, which cuts the 218-bp amplicon into two fragments of 193 and 25 bp. In amplicons harbouring the c.1222C>T mutation, a second NlaIII site is created that cuts the 193-bp fragment into two smaller fragments of 148 and 45 bp. Fragment sizes (bp) are shown on the left; (D) amino acid alignment of NDUFS1 orthologues. Alignments were generated with ClustalW using GenBank sequences from Mus musculus (NP_663493.1), Rattus norvegicus (NP_001005550.1), Homo sapiens (NP_004997.4), Pan troglodytes (XP_516047.2), Canis lupus familiaris (XP_859697.1), Bos taurus (NP_777245.1), Danio rerio (NP_001007766.1), Drosophila melanogaster (NP_727255.1), Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_568550.1), Oryza sativa (NP_001051072.1) and Caenorhabditis elegans (NP_503733.1). Position p.408 (Homo sapiens) is indicated. Conserved sites are indicated (asterisk).