Figure 3.
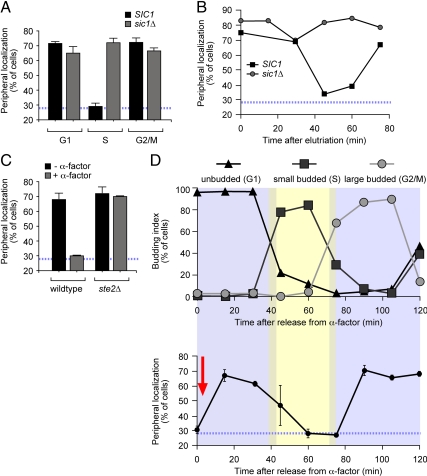
Cdk inhibitors negatively regulate gene recruitment to the nuclear periphery. (A) Wild-type (■) and sic1Δ mutant (▩) cells grown under activating conditions were scored for INO1 localization in cells with no buds (G1), small buds (S) or large buds (G2/M) as in Figure 1. (B) Newly born wild-type and sic1Δ mutant cells grown under activating conditions were recovered by centrifugal elutriation, and the localization of INO1 was scored at the indicated times. (C) Wild-type and ste2Δ mutant cells were grown under activating conditions in the presence (▩) or absence (■) of alpha factor. The population was scored for INO1 localization with respect to the nuclear periphery. (D) Alpha factor–arrested cells were washed into fresh activating medium lacking alpha factor at time 0 (red arrow) and INO1 localization (bottom panel) and budding index (top panel) were scored at the indicated times. The blue, hatched line represents the level of colocalization of the lac repressor spot with the nuclear envelope predicted by chance (Brickner and Walter, 2004).