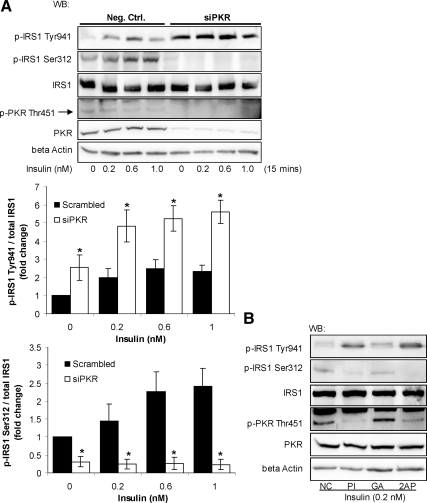
Figure 1.
Involvement of PKR in regulating the phosphorylation of IRS1. Reverse transfection of suspended HepG2 cells was performed with scrambled siRNA (negative control) or siRNA of PKR for 24 h, and the transfected cells were cultured in regular media for another 24 h (A). Cells were then treated with different concentrations of insulin for 15 min and harvested after the treatment (A). HepG2 cells were exposed to 5 μM PKR inhibitor (PI) or its analogue as a negative control (NC) or 10 mM 2-AP dissolved in PBS:glacial acetic acid (200:1; GA, control) for 12 h followed by the treatment of 0.2 nM insulin for 15 min (B). Western blot analysis was performed to detect the levels of β-actin and PKR and the total and phosphorylated levels of PKR and IRS1. The phosphorylation levels of IRS1 at Ser312 and Tyr941 were quantified by normalizing to total IRS1 levels and are expressed as the average of three samples ± SD from three independent experiments (A, middle and bottom). Student's t test was performed for analyzing the differences between samples transfected with siPKR and scrambled siRNA (negative control; A). Significantly higher (Tyr941) or lower (Ser312) than negative control; i.e., scrambled siRNA; *p < 0.01.