Figure 2.
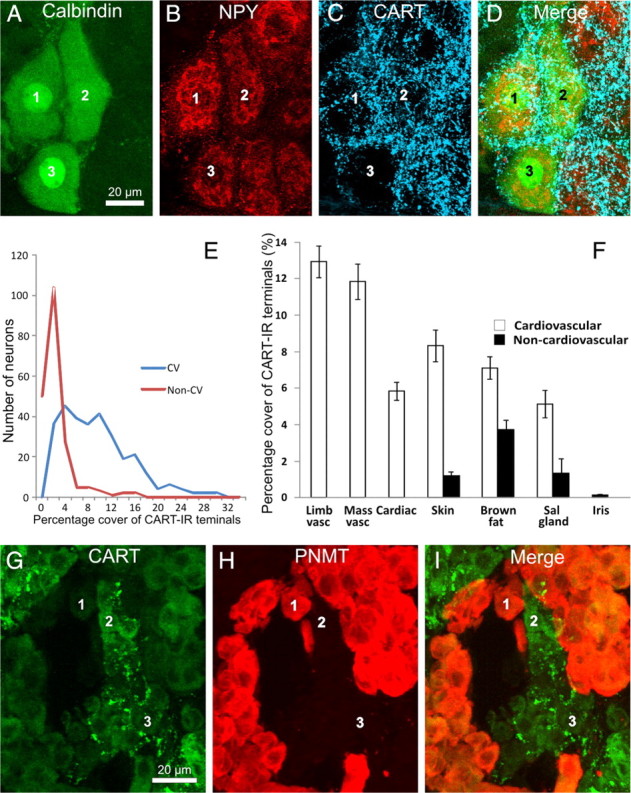
All images are projected z-series of confocal images. A–D, Stellate ganglion section showing cardiac-projecting postganglionic neurons (labeled 1–3), identified by their immunoreactivity to calbindin (A) and NPY (B) and by their location in clusters on the medial edge of the ganglion. All three cells are surrounded by dense arrays of CART-immunoreactive terminals (C). E, Frequency distribution of the innervation scores of all cardiovascular (blue line, CV) and non-cardiovascular (red line, Non-CV) neurons analyzed. The pooled cardiovascular neurons have strikingly higher range of innervation scores. F, Analysis of the innervation scores of CART-IR terminals surrounding functionally identified postganglionic neurons in the rat SCG and stellate ganglion. The area of CART-IR terminals surrounding each cell is shown. Neurons were retrogradely labeled from the forelimb muscle (Limb vasc), masseter muscle (Mass vasc), forelimb skin (Skin), interscapular brown fat (Brown fat), submandibular salivary gland (Sal gland), and anterior eye chamber (Iris). Retrogradely labeled neurons were identified by a combination of projection and immunoreactivity to NPY. Neurons projecting to the heart (Cardiac) were identified by a combination of topography and chemistry. CART-IR terminals are clearly associated with cardiovascular postganglionic neurons (white bars) but not non-cardiovascular neurons (black bars). Non-cardiovascular neurons in the skin, brown fat, and salivary gland represent pilomotor, thermogenic, and secretomotor neurons, respectively. Error bars are ±SEM. G–I, Rat adrenal gland, stained for CART immunoreactivity (G), PNMT immunoreactivity (H), and an overlay of the two images (I). Note that noradrenergic chromaffin cells lacking PNMT immunoreactivity are associated with CART-immunoreactive terminals in G. The same cells are labeled 1–3 in each series of image.
