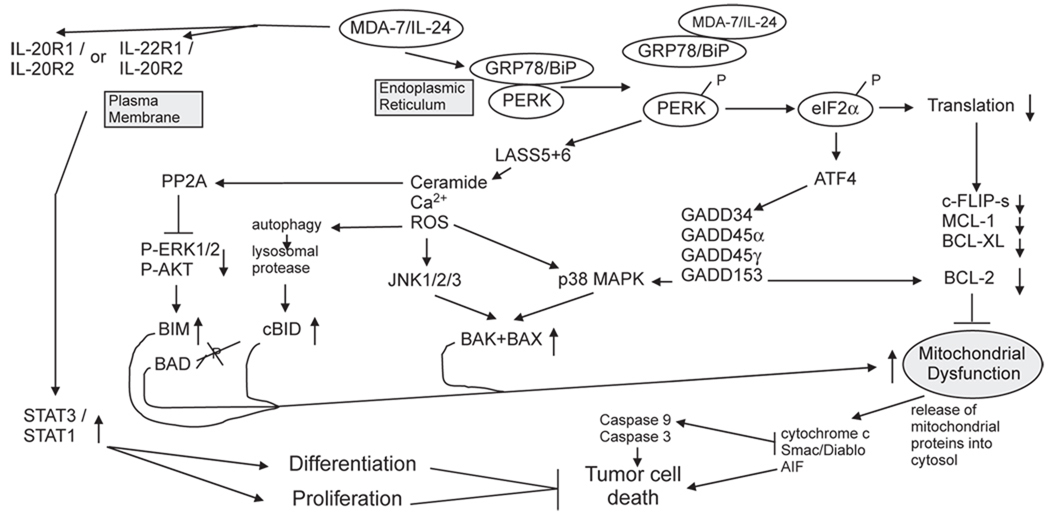
Fig. 1.
Molecular pathways by which MDA-7/IL-24 regulates cell viability and cell growth. MDA/IL-24 has two major targets in cells: the IL-20/IL-22 receptor complexes and the HSP70 family chaperone GRP78/BiP. MDA-7/IL-24 binding to its cognate receptors activates STAT family transcription factors and activation of these factors can promote differentiation and proliferation in a cell type dependent manner. STAT transcription factors play no role in MDA-7/IL-24 toxicity. MDA-7/IL-24 binds to GRP78/BiP; it is possible that entry of bacterial synthesized GST-MDA-7 into tumor cells is mediated by binding to cell surface GRP78/BiP. The majority of GRP78/BiP is present in the endoplasmic reticulum and is bound to PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK); the chaperone inhibits PERK kinase activity. MDA-7/IL-24 disrupts the association of GRP78/BiP with PERK permitting PERK to phosphorylate eIF2α; phospho-eIF2α suppresses the translation of the majority of cellular proteins resulting in the rapid loss of protective proteins that have short half lives such as MCL-1 and BCL-XL, and via ATF4 promotes the transcription of a specific subset of genes e.g. GADD34 that promote apoptosis. PERK signaling promotes increased LASS6 (ceramide synthase 6) levels that promote increased Ca2+ mobilization leading to elevated ROS levels. Increased ceramide/Ca2+/ROS activate JNK and p38 signaling that promotes activation of the toxic BH3 domain proteins BAX and BAK.