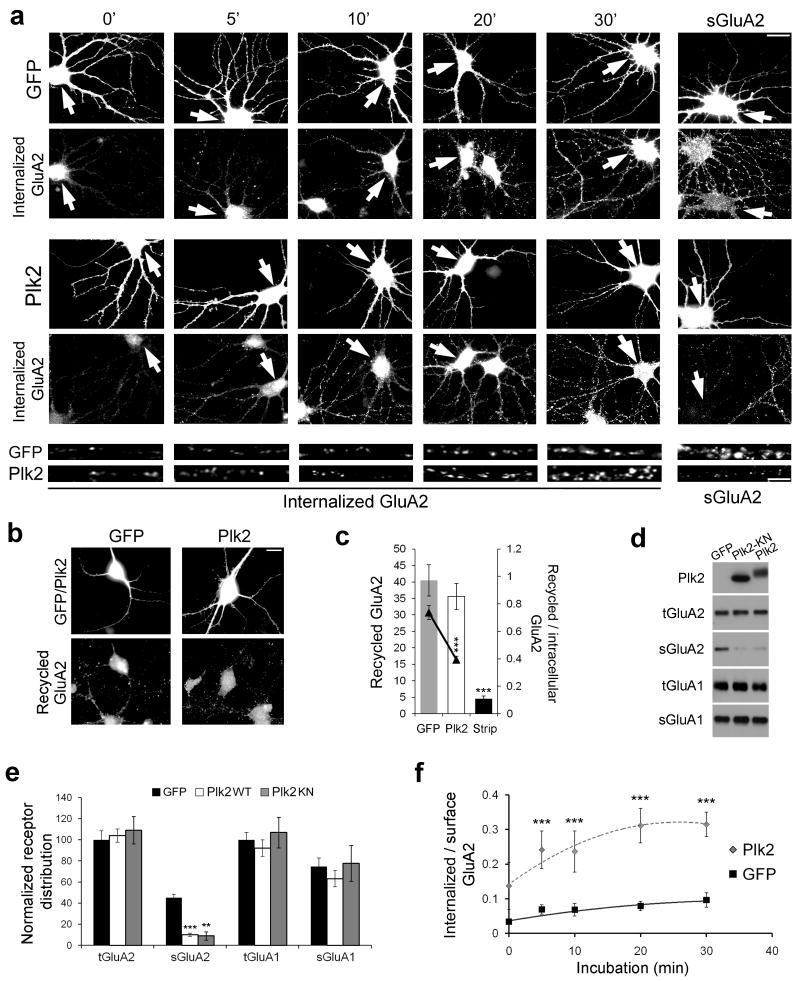
Figure 5. Plk2 controls GluA2 endocytosis and recycling.
(a) Time-course of GluA2 internalization following 18–20 h expression of Sindbis virus-expressed GFP or Plk2. Immunolabeling of infected neurons (GFP or Plk2) and internalized GluA2 or steady-state sGluA2 are indicated. Bottom, higher magnification views of representative dendrites for Sind-Plk2- or Sind-GFP-infected neurons. Arrows indicate infected neurons. Scale bars, 10 μm (wide view), 5 μm (magnified). (b) GluA2 recycling shown 30 min after acid strip of remaining surface labeling. Immunolabeling of infected cells (GFP or Plk2, top row) and recycled GluA2 (bottom row) are shown. (c) Quantification of (b); control with acid strip and no incubation time to allow for recycling (‘Strip’) demonstrates successful stripping of remaining surface primary antibody. Ratio of recycled receptor to available intracellular receptor is shown by line graph on secondary axis. (d) Surface biotinylation of cultured hippocampal neurons. Sister cultures were infected with Sind-GFP, Sind-Plk2-KN, or Sind-Plk2 for 20 h and cell surface proteins were biotin-labeled, isolated with avidin-beads, and immunoblotted for total and surface GluA2 (tGluA2 and sGluA2), total and surface GluA1 (tGluA1 and sGluA1), and Plk2 as indicated. No Plk2 was detected in surface fractions (not shown). Both Plk2-KN and Plk2 significantly reduced sGluA2. (e) Quantification of data from (d), normalized to total receptor expression in GFP control cells. (f) Quantification of (a) plotted as ratio of internalized to available surface GluA2 immunofluorescence; N=18–25 neurons per condition. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.