FIG. 1. Soman-induced ictal activity in the BLA and interictal activity in the hippocampus are synaptically driven.
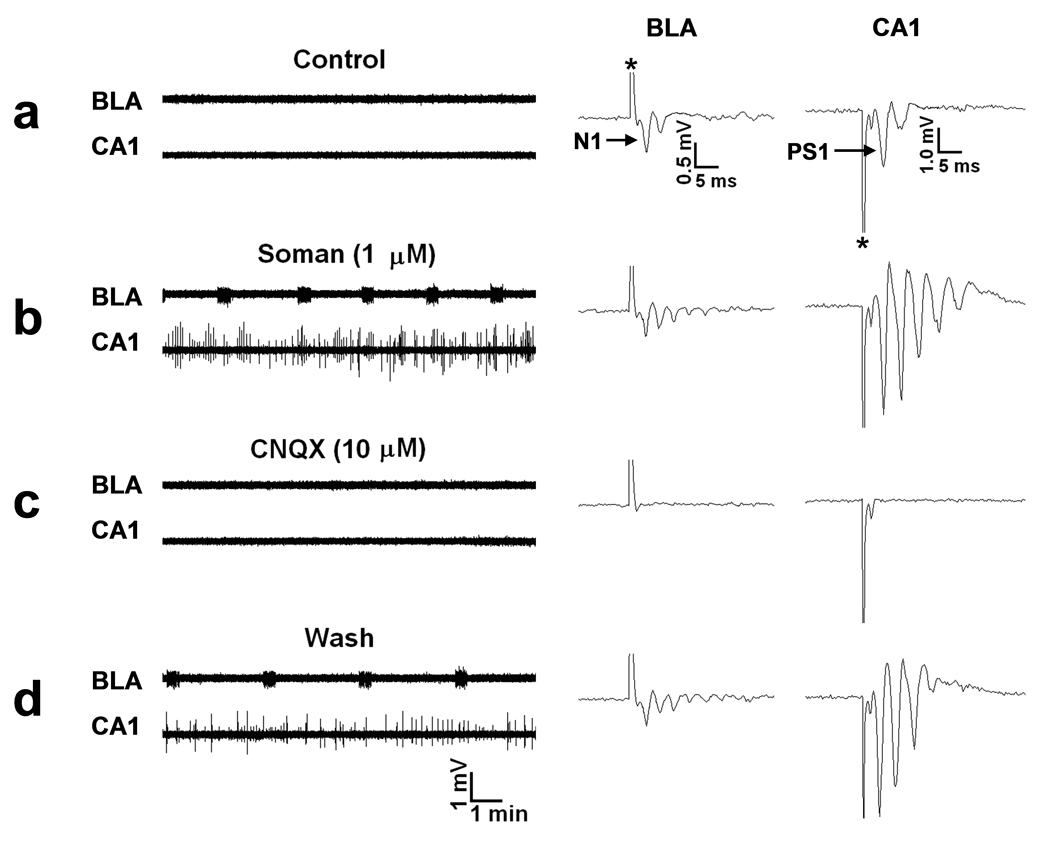
Extracellular field recordings, in gap-free mode, were simultaneously obtained in the BLA and the stratum pyramidale of the CA1 hippocampal area, in slices containing both regions. In this and the subsequent figures, the stimulus artifacts in the evoked field potentials (right panels) are indicated with an asterisk. (a) Field potentials in the BLA, evoked by stimulation of the external capsule, consisted of one major negative component (N1), followed by one or more lower-amplitude, late components. In the CA1 area, field potentials evoked by stimulation of the Schaffer collaterals consisted of a large population spike (PS1), which was often followed by one or two smaller amplitude, negative components. No spontaneous activity was present in the BLA or the CA1 area. (b) Exposure to 1 µM soman for 30 min reduced the amplitude of N1 in the BLA, and induced spontaneous, prolonged episodes of synchronous neuronal discharges resembling brain seizures. In response to soman exposure, the CA1 area produced additional population spikes in the enhanced evoked response, as well as spontaneous, interictal-like bursts. (c) Bath application of 10 µM CNQX (an AMPA/kainite receptor antagonist) blocked all synaptically-evoked components of the field potentials, as well as the BLA seizures and the CA1 interictal spikes. (d) The effects of CNQX were reversible.
