FIG. 3. Soman-induced interictal spikes in the hippocampus are reduced by a GluR5KR antagonist.
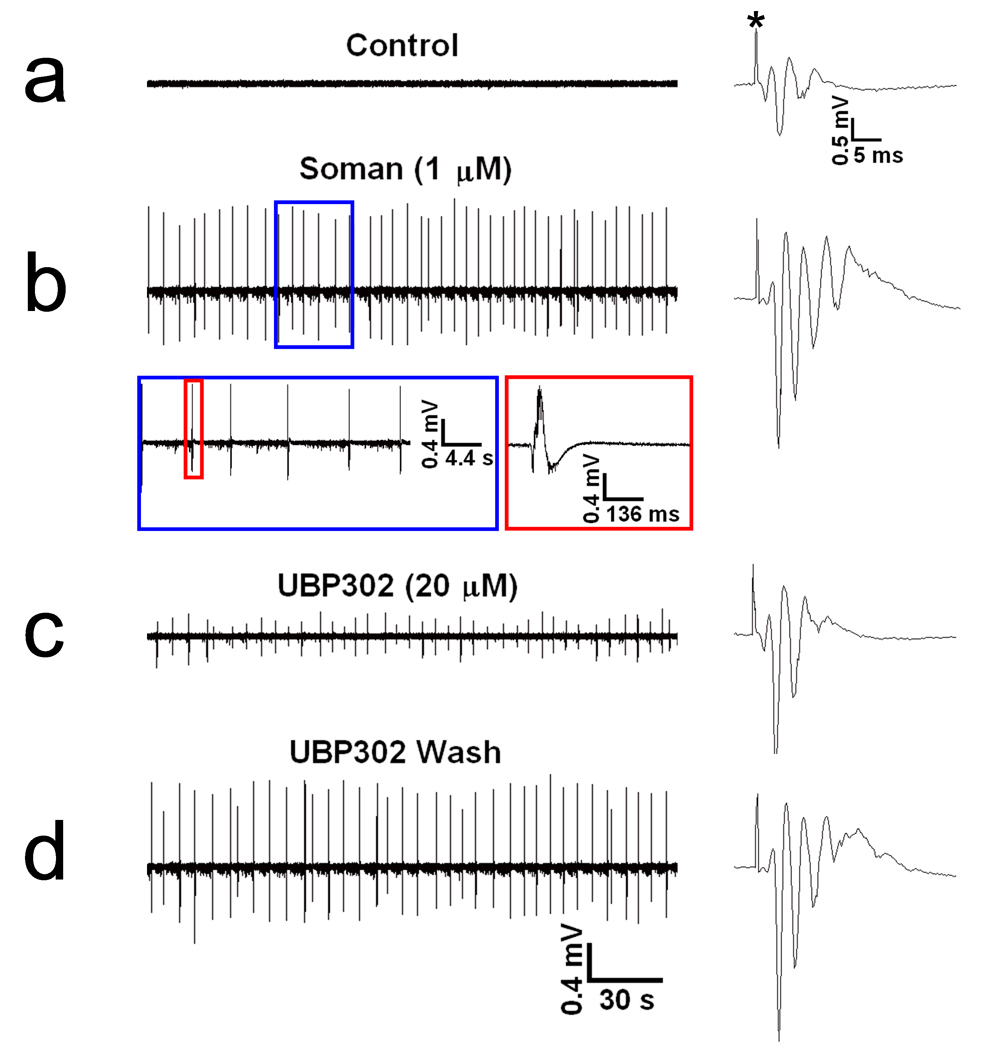
The extracellular field recordings presented here are from the pyramidal cell layer of the CA1 hippocampal area; in this experiment the BLA did not produce spontaneous activity in response to soman and, for this reason, it is not shown. (a) In control conditions there was no spontaneous activity, while the evoked field potential consisted of PS1 and a second, smaller population spike. (b) Exposure to 1 µM soman for 30 min increased the number of population spikes in the evoked field potential and induced spontaneous interictal-like spikes, within 7 min of exposure; these spikes were unaffected by soman washout. The section of trace b within the blue rectangle is shown with an expanded time base, and the spike within the red rectangle is shown on the right with the time base further expanded. (c) Bath application of 20 µM UBP302 reduced the amplitude of the spontaneous spikes, without affecting their frequency. (d) The effects of UBP302 were reversible.
