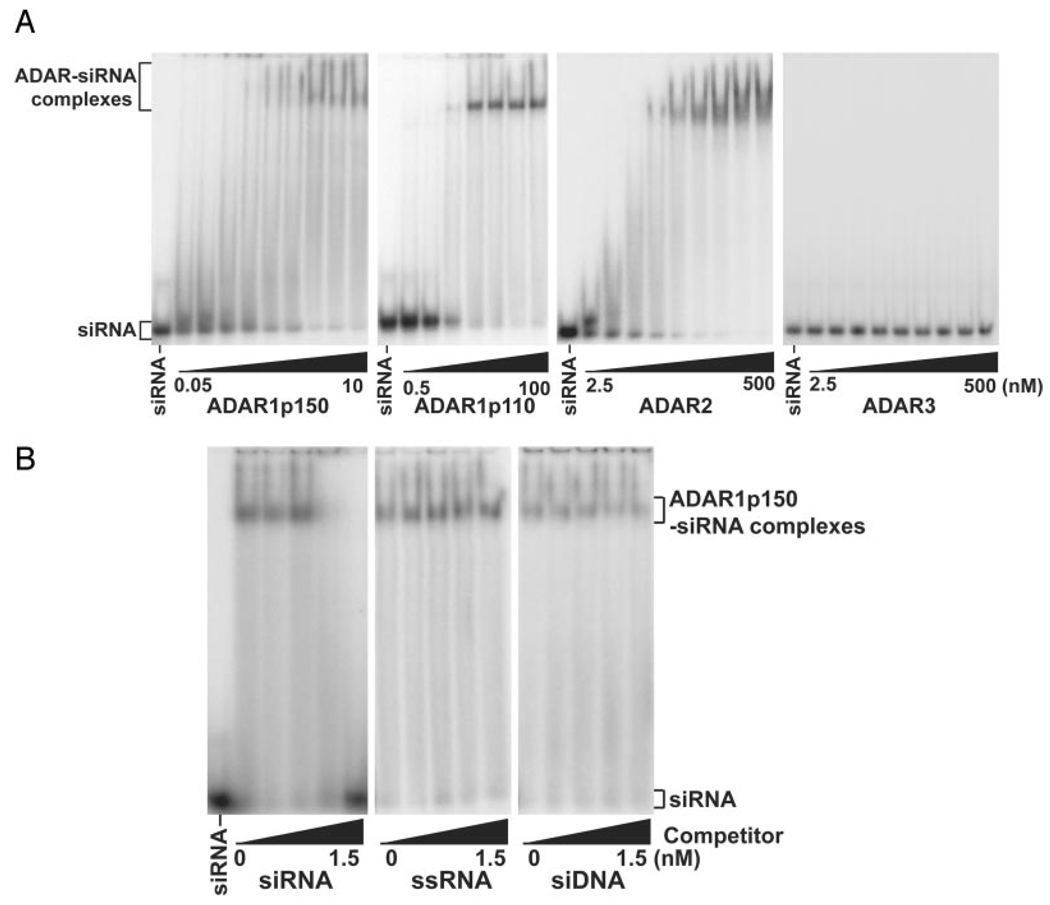
FIG. 2. High affinity binding of ADARs.
A, binding of homodimeric ADAR1 and ADAR2 to siRNA. Varying concentrations of FLAG-tagged ADAR1p150 (0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0,5, 1, 5, and 10 nm), ADAR1p110 (0.5, 1, 2, 10, 20, 50, and 100 nm), ADAR2 and ADAR3 (2.5, 5, 10, 15, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 nm) were examined by EMSA using a native 4% polyacrylamide gel. The 5′-end of the sense strand of 19-bp EGFP siRNA (10 pm) was labeled with 32P. The 5′-end of the antisense strand was also phosphorylated but without 32P. B, specificity of ADAR1 binding to siRNA. Competitive inhibition experiments were conducted by preincubating ADAR1p150 (5 nm) with varying concentrations of cold competitors (0, 0.05, 0.25, 0.75, and 1.5 nm) for 5 min prior to addition of 32P-labeled 19-bp siRNA probe (10 pm). siRNA, 19-bp EGFP siRNA; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA, the sense strand of the 19-bp EGFP siRNA; siDNA, dsDNA corresponding to the 19-bp EGFP siRNA.