Figure 3. Candidate IDTS can activate NF-κB.
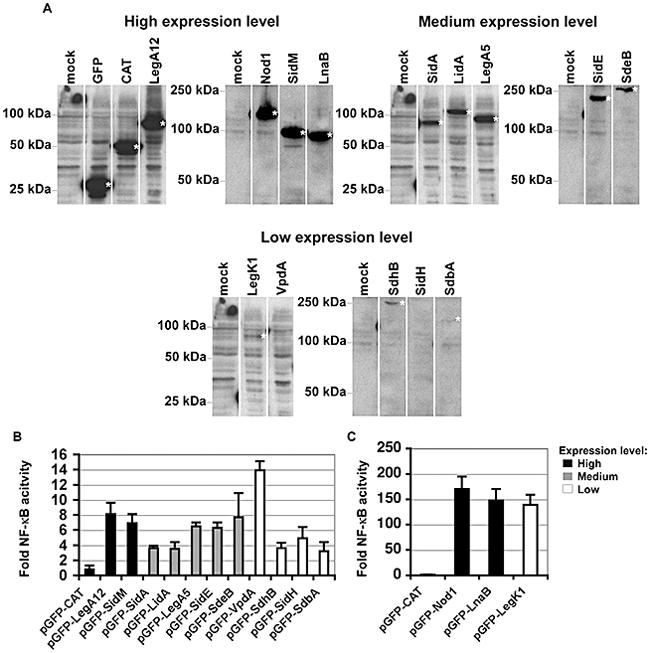
(A). Varied expression levels of L. pneumophila IDTS expressed in 293T cells. Protein expression levels of the indicated GFP fusions that had enhanced NF-κB activation are displayed on immunoblots, probing with anti-GFP. To allow clearer comparisons of the relative increases in NFκB activity, IDTS are grouped according to their expression levels in HEK293T cells. (B) Low level activation of NF-κB by L. pneumophila IDTS. Legionella NF-κB activators fused to GFP are marked on the x-axis. Shown are those IDTS that show statistically significant activation of NF-κB (T-test p-value ≤ 0.05). Bars representing those IDTS expressed at high levels are marked in black. Medium and low expression levels are shown in grey and white, respectively. (C) High level NF-κB activation by two Legionella IDTS. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with 200 ng of pNFκB-luciferase reporter and either 50 ng of the control plasmid (pGFP) or the indicated pGFP fusions and luminescence was assayed at 24 hours. pGFP-CAT (chloramphenicol aminotransferase) served as a negative control and pGFP-Nod1 was used as a positive control for NF-κB activation. Fold NF-κB activity is the relative light units of pGFP fusion compared to the pGFP control. Data represents the mean ± SE from three independent experiments preformed in triplicate.
