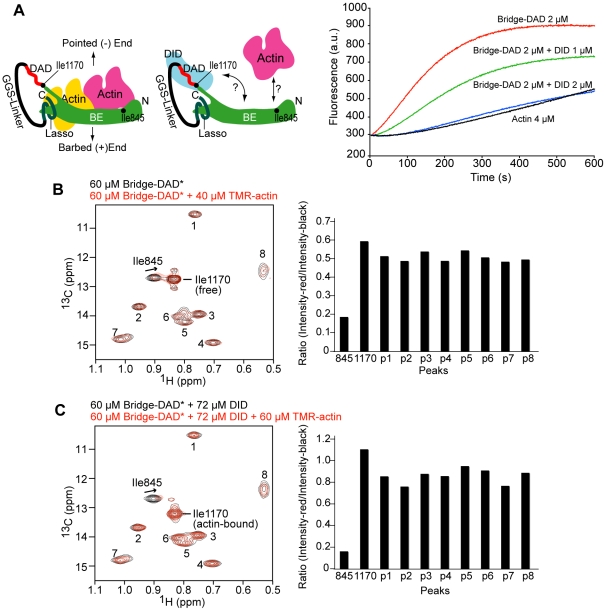
Figure 4. BE-DAD is inhibited by DID but actin monomer is accessible to the knob site.
(A) Pyrene actin assembly assays indicating that DID inhibits BE-DAD-stimulated actin assembly. A cartoon representing the artificial BE-DAD construct is shown on the left. (B, C) 1H-13C Ile δ1 methyl-TROSY HMQC spectra of 60 µM BE-DAD in the absence (B) or presence (C) of 72 µM DID are shown in black. The spectra in the presence of TMR actin are shown in red. Asterisk indicates the isotope-labeled material (BE-DAD) and others are unlabeled. In both (B) and (C), addition of TMR actin causes broadening and small shifts of the Ile845 resonance, indicating binding. Ile845 is located in the center of the knob actin binding site (Fig. 2C and refs. [20], [21]). The Ile1170 peak shifts upon addition of DID to BE-DAD (from (B) to (C)) because Ile1170 contacts the DID as shown in Fig. 2D. Ratios of the intensities of red/black peaks are plotted for each peak on the right panels. The ratios for the Ile845 peaks are significantly smaller than the other peaks in both (B) and (C), strongly suggesting that Ile845 interacts with actin.