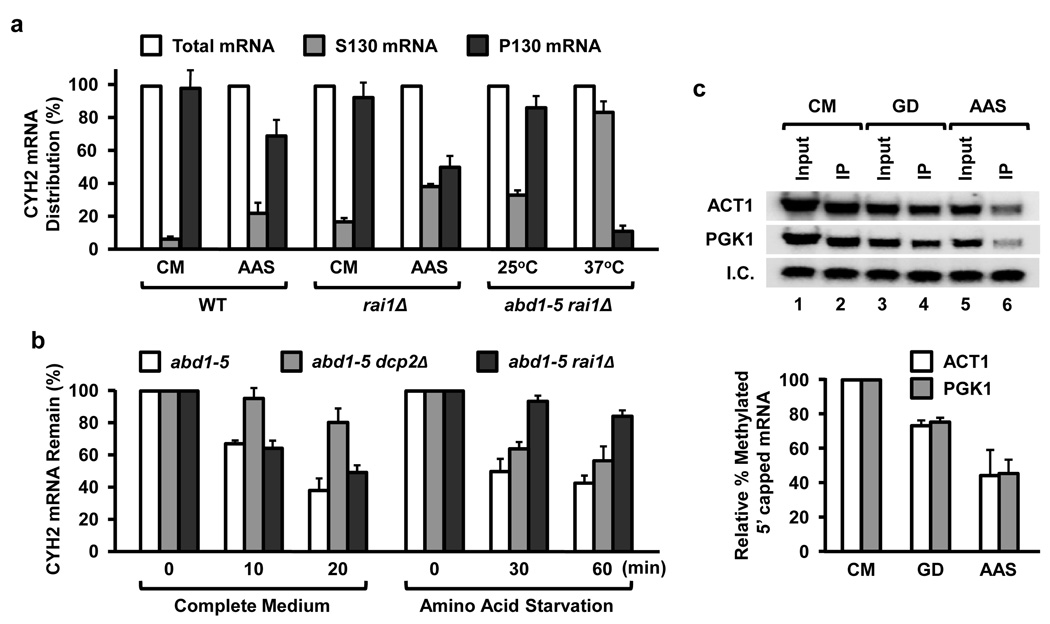
Figure 4. Aberrantly capped mRNA levels increase in cells exposed to nutrient starvation.
(a) Amino acid starvation shifts mRNAs into the soluble mRNP fraction. The mid-log phase yeast strains were shifted to the indicated medium and grown for 45 min prior to fractionation. RNA was isolated from polysome-containing fractions sedimenting at 130,000 × g (P130) and the supernatant (S130) fraction, which contained the soluble mRNP. Distribution of the CYH2 mRNA from each fraction was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. The abd1–5 rai1Δ double mutant strain grown at the permissive 25°C (methylated capped mRNA) or non-permissive 37°C (unmethylated capped mRNA) were used as a positive control. Results of three independent experiments are presented with error bars denoting +/− SD. (b) Aberrantly capped mRNAs are minimally affected by the Dcp2 decapping enzyme. The indicated strains were grown in complete medium at 22°C to an OD600 of 0.6 and subsequently cultured in the same medium or amino acid minus medium for 45 min followed by the addition of thiolutin. The levels of CYH2 mRNA were determined by quantitative RT-PCR as in (a) above. (c) Methylated capped RNA was immunopurified utilizing monoclonal anti-trimethylguanosine antibody column from cells grown at the denoted culture conditions for 45 min and were detected by Northern Blot analysis. Quantitations for the mRNA cap methylation were normalized to total input RNA and 32P-labeled methylated capped pcP RNA internal control (I.C.) and derived from three independent experiments. The error bars represent +/− SD.