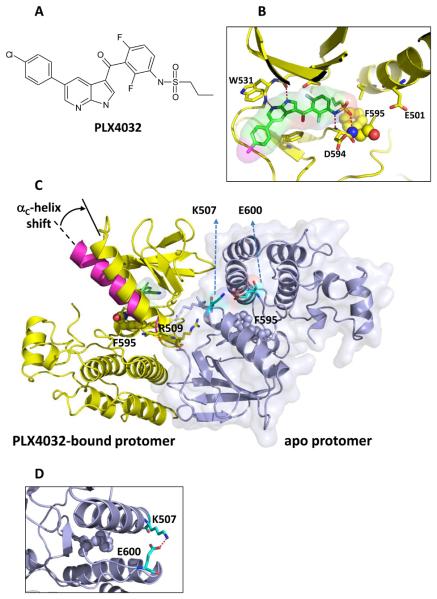
Fig 1. Three-dimensional structure of PLX4032 binding to B-RAFV600E.
A: The chemical structure of PLX4032.
B: Structure highlights the interactions of azaindole with the kinase hinge and the sulfonamide with the DFG loop, with F595 rendered in balls and other key protein residues shown as sticks.
C: The structure of the asymmetric dimer of B-RAFV600E is shown with the PLX4032-protomer bound to PLX4032 colored yellow (consistent with panel B). The surface outline of the other protomer (blue) is shown lightly shaded. Highlighted residues are R509 to reflect its role in anchoring the dimer and F595 to show that both protomers are in the DFG-in state. The αc-helix shown in magenta is overlaid on the PLX4032-bound protomer to show its typical configuration in an unoccupied protomer; the binding of PLX4032 causes a shift of the αc-helix as noted by the arrow.
D. Magnified view of the salt bridge between Lys-507 and Glu-600 that helps prevent compound binding to the apo protomer.