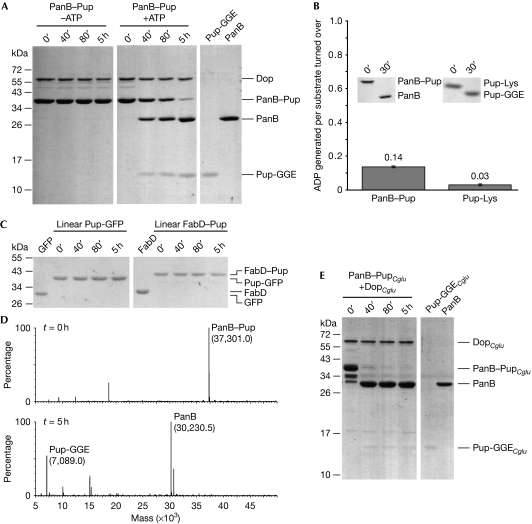
Figure 2.
Dop specifically cleaves the isopeptide bond between Pup and the substrate lysine residue. (A) PanB–Pup (3 μM)—a substrate modified with Pup using the ligase PafA—is depupylated by Dop (0.5 μM) only in the presence of ATP as analysed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie staining (first two panels). The expected amounts of Pup (3 μM) and PanB (3 μM) after complete cleavage are shown in the right panel. (B) Depupylation activity of Dop does not require stoichiometric ATP turnover. PanB–Pup (20 μM) or Pup-Lys (20 μM) were incubated in the presence of DopCglu (10 or 4 μM) and ATP (50 μM). Nucleotides were analysed after completion of the depupylation reaction (see inset). Error bars represent s.d. values from three experiments. (C) Pup-GFP (3 μM) and FabD–Pup (1.5 μM), in which Pup is amino-terminally fused to the substrates, are not depupylated by Dop (0.5 μM). (D) Depupylation reaction as described in (A) analysed by ESI-MS at t=0 h (upper panel) and t=5 h (lower panel). The theoretical masses are: 37,300.7 (PanB–Pup), 30,229.3 (PanB) and 7,089.4 (Pup-GGE). (E) PanB–PupCglu is depupylated by Corynebacterium glutamicum Dop (DopCglu). Assay conditions were as described under (A). C. glutamicum proteins are labelled with the subscript Cglu. Dop, deamidase of Pup; ESI-MS, electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry; GFP, green fluorescent protein; Pup, prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein; SDS–PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.