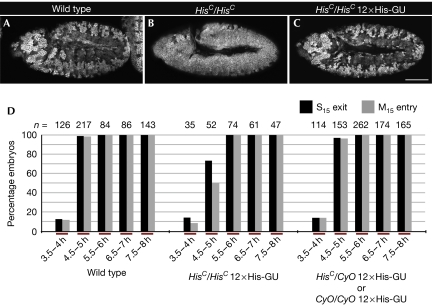
Figure 2.
Rescue of HisC by 12 His-GUs. (A–C) Representative embryos from time-matched collections 4.5–5 h after egg laying stained for Cyclin B. Wild-type embryos undergo M15 in the dorsal epidermis (A), whereas HisC mutant embryos are blocked with high levels of Cyclin B before M15 (B). In the presence of 12 transgene-based His-GUs, HisC mutant embryos display a wild-type M15 pattern (C); wild type refers to w− control. (D) The percentage of embryos that completed S15 (S15 exit) or progressed into M15 (M15 entry) in the dorsal epidermis was determined. Embryonic collections were time matched for the indicated time interval after egg laying. The left set of columns are wild type. The middle display HisC homozygotes rescued by 12 His-GUs and the right display embryos from the same collection, which were not homozygous HisC mutant. These embryos acted as internal controls to ensure reproducible timing of the collections. For details on classification of embryos see supplementary Fig S5 online. Scale bar, 100 μm (A–C); anterior left (A–C), His-GU; histone gene repeat unit; M15, mitosis 15; n, number of embryos.