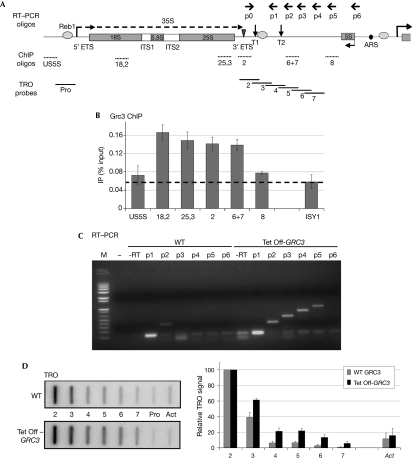
Figure 2.
Grc3 depletion results in defective transcription termination by RNA polymerase I. (A) Schematic of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae rDNA repeat. In addition to the sequence encoding 18S, 5.8S and 25S rRNA (grey rectangles), the Pol I transcription unit includes ETSs and ITSs; the 35S primary transcript is shown as a dashed arrow. Grey ovals denote binding sites for Reb1, the triangle denotes the Rnt1 cleavage site and vertical arrows indicate T1 and T2 terminator elements. 5S rDNA, transcribed by Pol III in the opposite orientation, and ARS are shown. Primers used for RT–PCR are shown above, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) oligonuleotides and TRO probes below. (B) ChIP analysis of 3HA-tagged Grc3 along rDNA. Specific enrichment (above dashed line) is visible over the rRNA encoding and terminator sequence. Pol II-transcribed ISY1 is shown as a control. An average of two independent experiments is shown, error bars indicate s.d. values. (C) RT–PCR analysis of transcripts downstream to the Rnt1 cleavage site in WT or Grc3-depleted (Tet Off-GRC3) cells. Reverse transcription was primed with oligonuleotides p1–p6, PCR with the common forward primer p0 and the indicated reverse primers. Grc3 depletion results in stabilization of the Pol I transcripts over the 35S 3′-region. Oligonucleotide p1 and no reverse transcriptase (−RT) or no cDNA were used as a template in control PCR reactions. M, molecular weight marker (Invitrogen 1 kb Plus). (D) TRO analysis of Pol I transcripts over the 35S 3′-region in WT or Tet Off-GRC3 cells. Grc3 depletion results in a Pol I termination defect. Quantification of the signals is shown in the right-hand panel. Background signal (Pro) was subtracted to each probe value. Data were then normalized towards probe 2, set to 100%. The Pol II-transcribed actin gene (Act) is shown as a control. The average of three independent experiments is shown, error bars indicate s.d. values. ARS, autonomously replicating sequence; ETS, external transcribed sequence; HA, haemagglutinin; ITS, internal transcribed sequence; RT–PCR, reverse transcriptase PCR; rDNA, ribosomal DNA; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; TRO, transcriptional run on; WT, wild type.