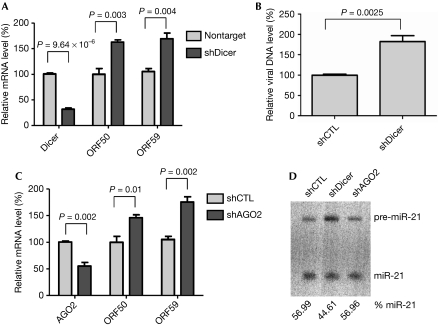
Figure 1.
Blocking microRNA biogenesis induces Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic gene expression. BC-3 cells were transduced with lentiviral shRNAs targeting Dicer or AGO2 and selected with puromycin. (A) Knocking down Dicer induces viral lytic genes expression. The mRNA levels of Dicer, the KSHV lytic genes, ORF50 and ORF59, were quantified by RT–qPCR. (B) Knocking down Dicer induces viral lytic DNA replication. BC-3 cells were transduced with lentiviral Dicer shRNA and selected with puromycin. KSHV DNA was quantified by real time–PCR to detect ORF26 genomic sequences. Viral DNA levels are normalized to samples transduced with control shRNA. (C) Knocking down AGO2 induces viral lytic gene expression. The mRNA levels of AGO2, the KSHV lytic genes, ORF50 and ORF59, were quantified by RT–qPCR. Data are normalized to the mRNA level of cells transduced with control shRNA. All data are normalized to GAPDH. Results represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (D) Depleting Dicer decreases production of mature miRNA. Northern blot analysis of miR-21 RNA from BC-3 cells transduced with lentiviral shRNAs targeting control shRNA, Dicer and AGO2. The relative levels of mature miR-21 RNA are shown below the blot. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; KSHV, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; mRNA, messenger RNA; miRNA, microRNA; RT–qPCR, reverse transcriptase–quantitative PCR; shCTL, control short hairpin RNA; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.