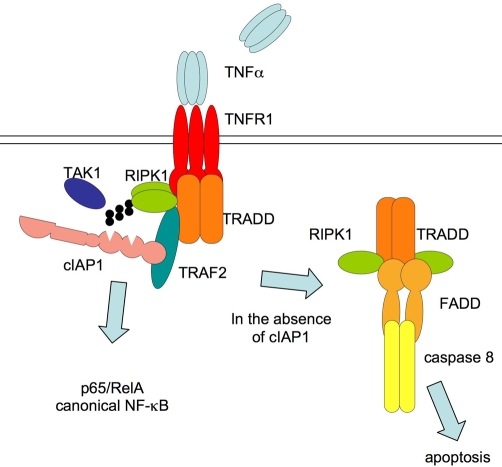
Figure 3. Signalling in response to tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is regulated by inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs).
When TNF binds to TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), it stimulates formation of a complex containing TRADD (TNFR superfamily 1A-associated via death domain), RIPK1 (receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 1), TRAF2 (TNFR-associated factor 2), cIAP1 (cellular IAP 1), and other proteins. RIPK1 becomes K63 ubiquitylated, inhibitor of kappa-B is phosphorylated and degraded, and the canonical nuclear factor-kappa-B (NF-κB) component p65/RelA is released and enters the nucleus. If cIAP1 is removed (by gene deletion or addition of an inhibitor of apoptosis antagonist compound), TNF triggers formation of a second complex containing TRADD, FADD (Fas-associated protein with death domain), RIPK1, and caspase 8, which become activated, leading to apoptosis. TAK1, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta activated kinase 1.