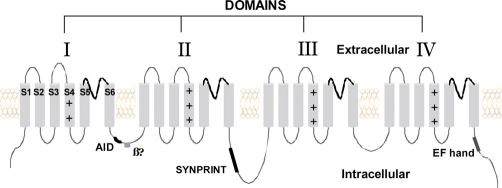
Figure 1. Two-dimensional schematic of the α-subunit of CaV2.1 showing functionally important regions of the peptide.
The subunit consists of four domains (I-IV), each containing six transmembrane segments (S1-S6). The S4 segment of each domain is lined with positively charged amino acids and acts as the voltage sensor. The S5-S6 interlinker forms the pore of the channel. The AID (alpha interaction domain) forms the binding pocket for the β-subunit of CaV2.1. The SYNPRINT (synaptic protein interaction) region interacts with SNARE (SNAP (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein) receptor) proteins such as syntaxin and SNAP-25, which are involved in synaptic transmission. Sites of G-protein modulation via βγ-subunits are shown along with the ‘EF’ hand, which is considered to be involved in calcium-dependent facilitation.