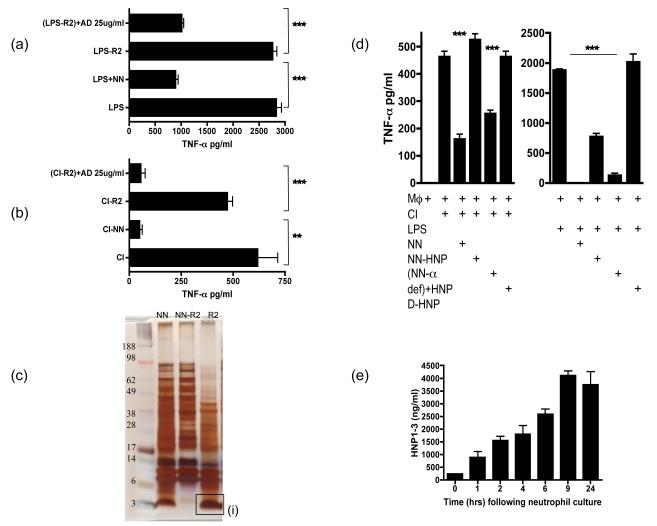
Figure 5. Alpha defensins are one of the the active anti-inflammatory factors released by apoptotic/necrotic neutrophils.
LPS (a) or CI (b) stimulated HMDM were cultured with NN, NN depleted of hydrophobic molecules by R2 beads (NN-R2) and NN-R2 where α-defensins were added back at 25ug/ml [(NN-R2)+AD]. Culture supernatants were collected after 18 hours of culture and tested for TNF-α secretion by ELISA. (c) A protein gel of NN indicated the large number of proteins released by necrotic neutrophils (NN). NN were depleted of hydrophobic proteins by R2 beads (NN-R2) and the proteins bound to the R2 beads (R2) were identified. R2 beads completely depleted a large band of small proteins between 3-5kD. This band was digested and sequenced by HPLC and identified as the anti-microbial peptides, α-defensins. (d) The actual release of α-defensins over 24 hours by cultured neutrophils undergoing apoptosis was quantified by HNP 1-3 ELISA. (e) To ensure that the R2 beads had not depleted other anti-inflammatory factors, α-defensins in NN were specifically depleted using anti-HNP antibodies bound to dynabeads. HMDMs were then stimulated with CI or LPS along with added NN depleted of α-defensins (NN-α def) or depleted NN where HNP 1-3 has been added back at 25ug/ml (NN-α def)+HNP. As an additional control HMDMs were stimulated with CI or LPS in the presence of the D-enantiomer of HNP1-3, which lacks anti-inflammatiory activity and is protease resistant.. *** p ≤0.0001, ** p ≤0.04. error bars =SEM.