Figs 1.
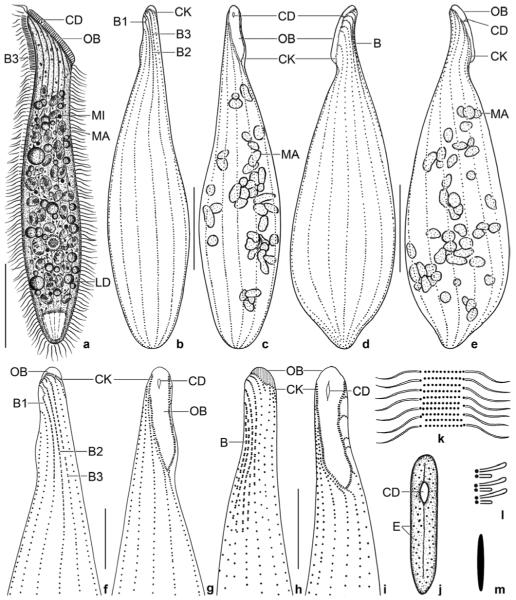
a–m. Spathidium alqasabi from life (a, j–m) and after protargol impregnation (b–i). a – right side view of a representative specimen, length 200 μm; b, c, f, g – ciliary pattern of dorsal and ventral side and macronucleus of holotype specimen, length 210 μm; d, e – infraciliature of left and right side of a strongly inflated specimen; h, i – dorsal and ventral view of a specimen with four dorsal brush rows; j – frontal view of oral bulge showing the conical depression; k – surface view showing cortical granulation; l – bristles of brush row 1; m – extrusome, length 4 μm. B (1–3) – dorsal brush (rows), CD – conical depression, CK – circumoral kinety, E – extrusomes, LD – lipid droplets, MA – macronucleus nodules, MI – micronucleus, OB – oral bulge. Scale bars: 50 μm (a–e) and 20 μm (f–i).
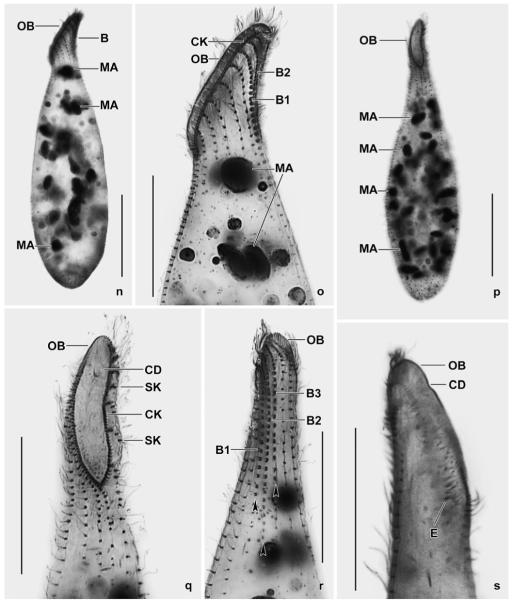
n–s. Spathidium alqasabi, morphology and ciliary pattern after protargol impregnation. n, o – left side views showing the scattered macronucleus nodules, the steep oral bulge, and part of the dorsal brush; p, q, s – ventral and lateral views showing the shape of the circumoral kinety, the scattered macronucleus nodules and, specifically, the conical depression near the dorsal end of the oral bulge; r – dorsal view with ends of dorsal brush rows marked by arrowheads. Rows 1 and 3 have a similar length, an unusual feature. B (1–3) – dorsal brush (rows), CD – conical depression in oral bulge, CK – circumoral kinety, E – extrusomes, MA – macronucleus nodules, OB – oral bulge, SK – somatic kineties. Scale bars: 50 μm (n, p) and 30 μm (o, q–s).