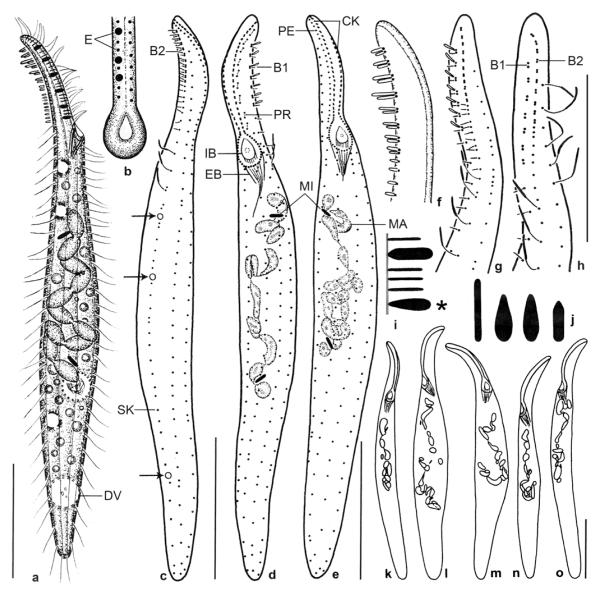
Figs 5a–o.
Pseudomonilicaryon brachyproboscis nov. spec. from life (a, b, f, i, j) and after protargol impregnation (c–e, g, h, k–o). a – right side view of a representative specimen, length 140 μm; b – frontal view of oral opening; c, d – dorsolateral and ventrolateral view of ciliary pattern and nuclear apparatus of holotype specimen, length 118 μm. Arrows mark the single excretory pore of the contractile vacuoles; e – ventrolateral view of ciliary pattern and nuclear apparatus of a paratype specimen. Note the narrowly ellipsoidal micronuclei; f – fine structure of dorsal brush; g, h – dorsal ciliary pattern of proboscis. Drawn to scale; i – two types of oral bulge extrusomes. Type I extrusomes are oblong with conical anterior end, 2.5 × 1 μm in size, and appear narrowly ovate when slightly out of focal plane (asterisk). Type II extrusomes are finely rod-shaped and 2 μm long; j – developing cytoplasmic extrusomes are rod-shaped (4 μm long), narrowly ovate to oblong (3 μm long), and oblong with conical anterior end (2.5 × 1 μm); k–o – variability of body shape and size as well as of nuclear apparatus. Drawn to scale. B1, 2 – dorsal brush rows 1, 2, CK – circumoral kinety, DV – defecation vacuole, EB – external basket, E – extrusomes, IB – internal basket, MA – macronucleus, MI – micronucleus, PE – perioral kinety, PR – preoral kinety, SK – somatic kinety. Scale bars: 30 μm (a, c–e, k–o) and 20 μm (g, h).