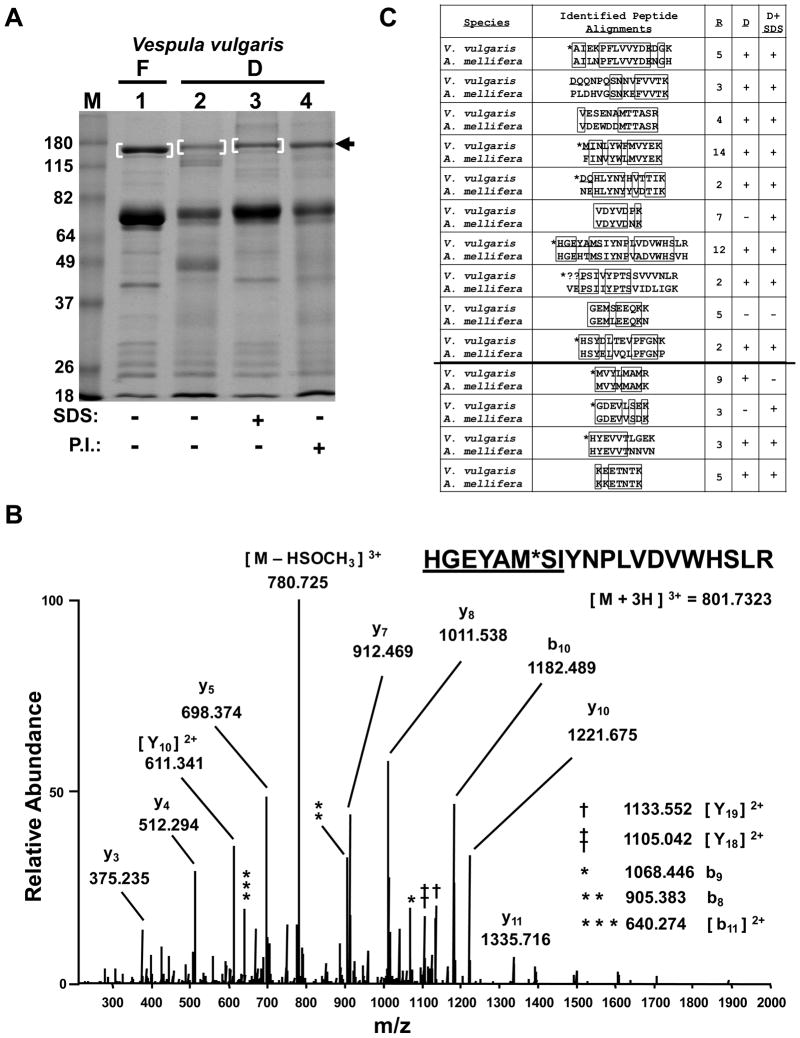
Figure 2.
Preservation of field samples for MS-based protein identification. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of V. vulgaris larval trophallactic fluid following a 3 week preservation period by either freezing or desiccation, with or without SDS or protease inhibitors (P.I.) as indicated. Bracketed regions and arrow indicate bands chosen for in-gel digestion and LC-MS/MS analysis. “F” and “D” indicate frozen and desiccated respectively. Molecular weight markers in lane “M” are in kilodaltons. The gel was stained with Coomasie. (B) Low energy, high resolution MS/MS spectrum acquired in the orbitrap for the indicated peptide as a triply-charged precursor. “*” indicates an oxidized methionine. The underlined sequence was manually extended from PepNovo results. See Supporting Information Table 1 for theoretical and observed m/z values for b- and y-type ions and (C) for alignment of this peptide with its ortholgous sequence in A. mellifera. (C) PepNovo-identified and manually-validated V. vulgaris peptides matches to the top protein identified, Larval-Specific Very High Density Lipoprotein) from (A) band 1, are aligned with orthologous sequences from A. mellifera. “R” indicates the number of times a given peptide was identified redundantly by PepNovo. “D” and “D + SDS” indicate whether the given peptide was also identified from (A) lanes 2 and 3 respectively. The line separating the final four peptides indicates additional PepNovo sequences not found in the 200 scoring peptides with a PepNovo score > 6 and mapping back to the top protein hit. “*” indicates that the isobaric isoleucine and leucine residues were designated to match the A. mellifera sequence. Boxes indicate amino acid identity. “??” indicates this sequence had an unsolved N-terminal extension of likely two residues.