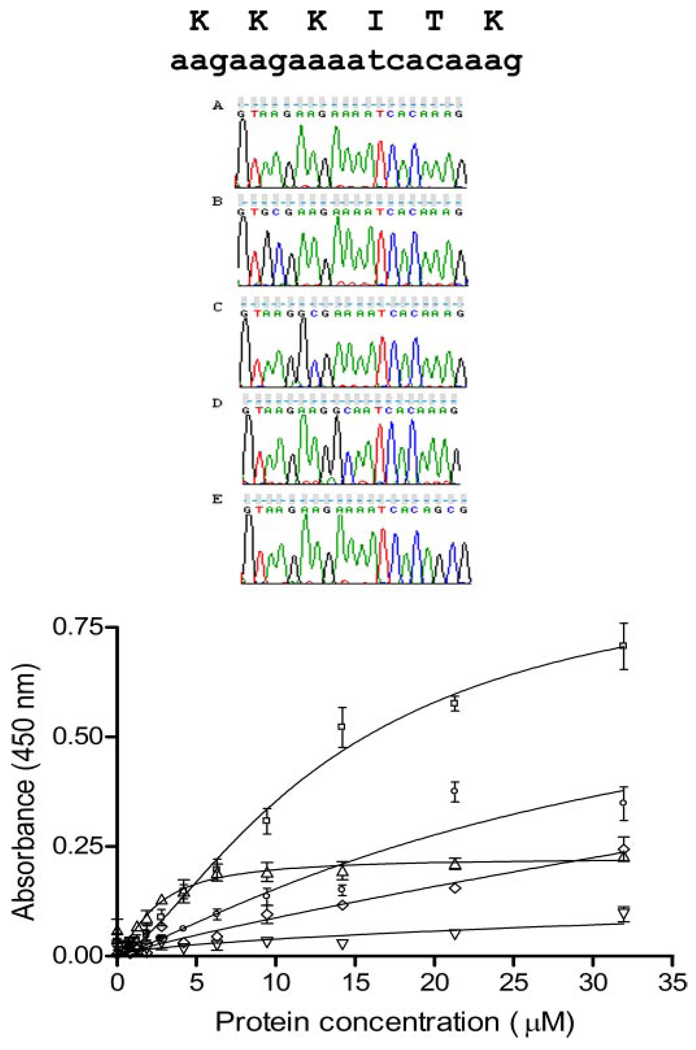
FIGURE 4. Relative affinities for heparan sulfate after site-directed mutagenesis.
Site-specific mutagenesis of heparan sulfate binding site 1. Upper panel, sequence verification of site-directed change in sequence. A, wild type sequence; B, K147A mutant; C, K148A mutant; D, K149A mutant; E, K152A mutant. Lower panel, heparan sulfate solid phase binding assay. Binding curves are shown for wild type amino-terminal domain fragment (NTD[p7], squares) and four mutants: K147A (triangles), K148A (inverted triangles), K149A (diamonds), K152A (circles). Specific binding is almost eliminated for K148A and K149A and decreased significantly for K152A. In contrast, a decrease in maximal binding with a decrease in nonspecific binding (nonsaturable binding) is observed for K147A with improvement of Kd(see Table 3).