Figure 4.
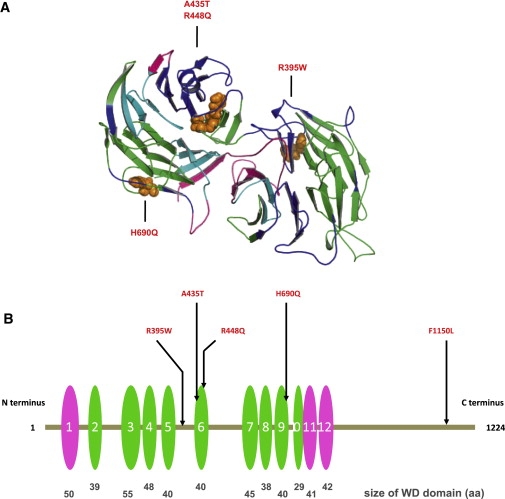
WDR11 Structural Model Indicating the Mutation Sites
(A) Model spanning amino acids 70–739 of WDR11. The model was obtained by alignment to 1NR0 via ClustalW and MOE (Molecular Operating Environment [MOE 2004.03], Chemical Computing Group, Montreal, Quebec, Canada H3B 3X3). WDR11 forms a double propeller structure, in which the WD domains indicated in (B) form the main structural constituent. The two propeller axes are tilted with respect to one another, so only the propeller structure on the left is clearly visible in this representation. Colors indicate side chains of the four mutations within the modeled sequence region, as follows: WD domains predicted on the basis of the model (green), on the basis of SMART (pink), or both (cyan). The sites of the mutations are indicated in orange.
(B) Positions of five missense mutations in WDR11; WD domains are depicted as ovals. The WD domains predicted on the basis of the model and by SMART are depicted in green and pink, respectively. The relative sizes and locations of WD domains are to scale. WDR11 contains twelve WD domains, nine (second to tenth repeats) that are confirmed on the basis of direct comparison with the template structure of AIP1 and three additional repeats (first, 11th, and 12th) detected by sequence comparison outside the region of the structural model. Note that three mutations directly affect WD domains 6 and 9.
