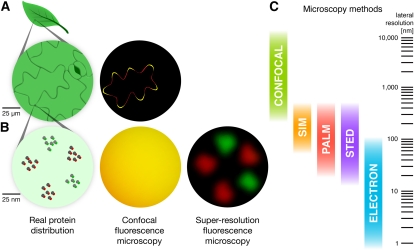
Figure 1.
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy can reveal PM subcompartmentalization that is unresolvable by conventional techniques. A, Confocal microscopy is sufficient to visualize localization patterns at a scale of hundreds of nanometers. Two hypothetical PM proteins are labeled with different fluorescent tags in a pavement cell. One localizes to the tips of the cell lobes (green), much as observed for the small G-protein ROP2 (Fu et al., 2005), and the other is dispersed more uniformly (red). The overlap appears as yellow. B, At the nanoscale, these proteins also cluster into disparate microdomains. Super-resolution microscopy is necessary to resolve the two types of microdomains. All images are simulated. C, Comparison of the spatial scales at which different microscopy techniques are useful.