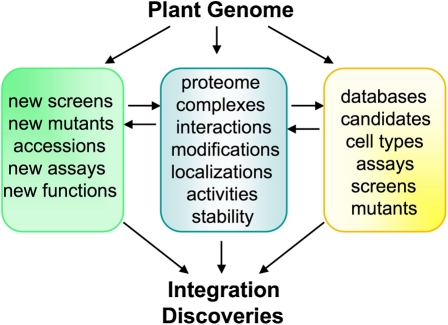
Figure 2.
Discover new cellular signaling pathways. All information for cellular signaling is embedded in the plant genome, which can be explored to discover and define signaling pathways and their interconnections through integrative approaches. The traditional genetic approach will be empowered with more specific and sensitive phenotypic screens to identify new mutants. Creative and thorough analysis of available natural variations/accessions and new assays for existing mutant collections will uncover new gene functions. The well-defined proteome with detailed information about protein complexes, interactions, modifications, localizations, activities, and stability will provide mechanistic and dynamic understanding of cellular signaling in plants. The growing power of comprehensive databases and computional analysis tools, from DNA, RNA, protein, to metabolite, will offer new ideas and predictions to select and characterize candidates in diverse signaling steps, and to integrate and model plant life. Finally, targeted mutagenesis and cell-type-specific and conditional mutants will be required for functional characterization of genes not currently accessible due to redundancy and lethality.