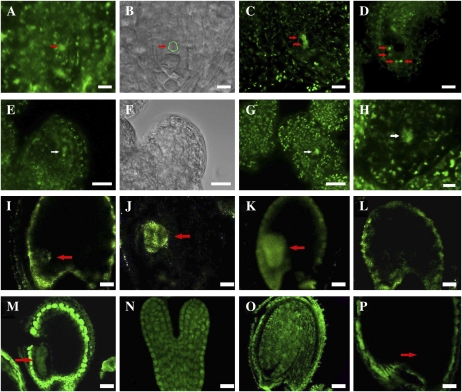
Figure 7.
Cellular distribution of CTF7 in wild-type and 35S-CTF7::YFP plants. A to D, 35S-driven CTF7::YFP localization during female gametophyte development. A, FG1 ovule. The arrow indicates the female gametophyte nucleus. B, Bright-field image of A. The position of the female gametophyte is circled. C, FG2 ovule. The arrows indicate nuclei. D, FG7 ovule. The arrows indicate nuclei. E to H, Aborted female gametophytes in 35S-CTF7::YFP plants. E, Aborted FG1 ovule. The arrow indicates degraded nucleus. F, Bright-field image of E. G, Aborted ovule at early FG1. The arrow indicates degraded nucleus. H, Aborted ovule. The arrow indicates remnants of degraded nucleus. I, Seed with globular-stage embryo from a genomic CTF7::YFP plant. J, Seed with heart-stage embryo from a genomic CTF7::YFP transgenic plant. K, Seed with torpedo-stage embryo from a genomic CTF7::YFP transgenic plant. L, Seed from a wild-type, negative control plant. M to P, CTF7 immunolocalization on whole-mount cleared seeds. M, Torpedo-stage embryo. N, Single embryo at early torpedo stage. O, Cotyledon-stage embryo. P, Negative control with no primary antibody. Arrows in I to K, M, and P denote the position of the embryo. Bars = 5 μm.