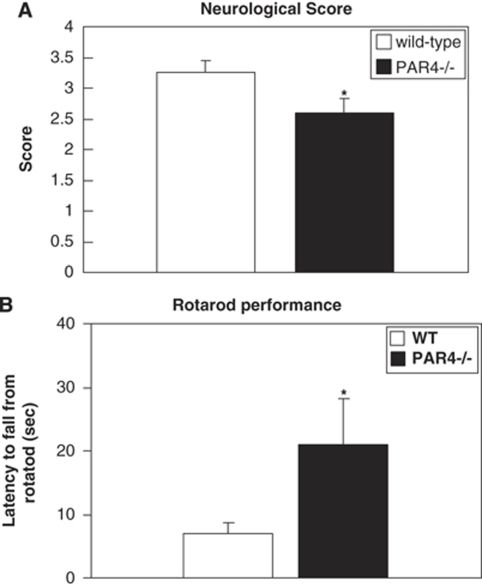
Figure 4.
Effect of PAR4 on neurologic function in mice subjected to I/R injury. (A) Neurologic score was evaluated after 1 h MCAO and 23 h reperfusion. (B) Rotarod testing of sensorimotor deficits in wild-type (n=8) and PAR4−/−(n=10) mice after 1 h MCAO and 23 h reperfusion was tested. Deficiency of PAR4 causes significantly improved both neurologic score and sensorimotor function compare to wild type. (*P<0.05; mean±s.e.m.).