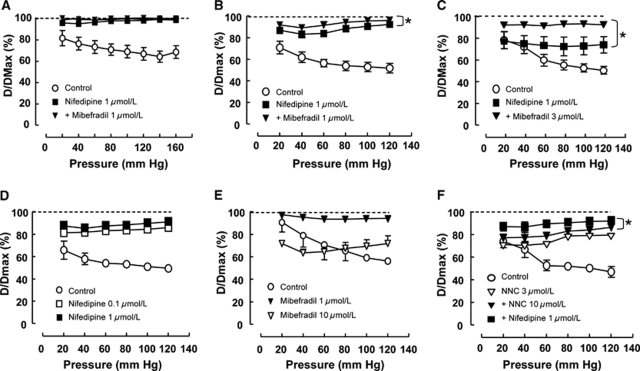
Figure 7.
Effect of L- and T-type blockers on myogenic tone of basilar artery (A) and branches (B–F). (A–C) Nifedipine-resistant tone increased with decreasing vessel size. In the main basilar artery (vessel diameter 319 μm), nifedipine (1 μmol/L) completely abolished vascular tone, and mibefradil (1 μmol/L) had no additional effect (A). In the larger branches (vessel diameter 172 μm), addition of mibefradil (1 μmol/L) after nifedipine (1 μmol/L) caused a further significant relaxation (B). In the smaller side branches (vessel diameter 101 μm), nifedipine (1 μmol/L) only partially reduced tone at pressures above 60 mm Hg and addition of mibefradil (3 μmol/L) significantly reduced tone at all pressures (C). (D–F) Effects of L- and T-type blockers in the larger branches of the basilar artery. Nifedipine (0.1, 1 μmol/L) caused a dose-dependent relaxation, but did not completely abolish tone (D). Mibefradil alone inhibited constriction at 1 μmol/L, but induced constriction at 10 μmol/L (E). The T-type blocker, NNC 55-0396, caused a dose-dependent inhibition of constriction that was further inhibited by the addition of nifedipine (1 μmol/L) (F). *P<0.05, two-way analysis of variance, n=4 to 6 vessels.