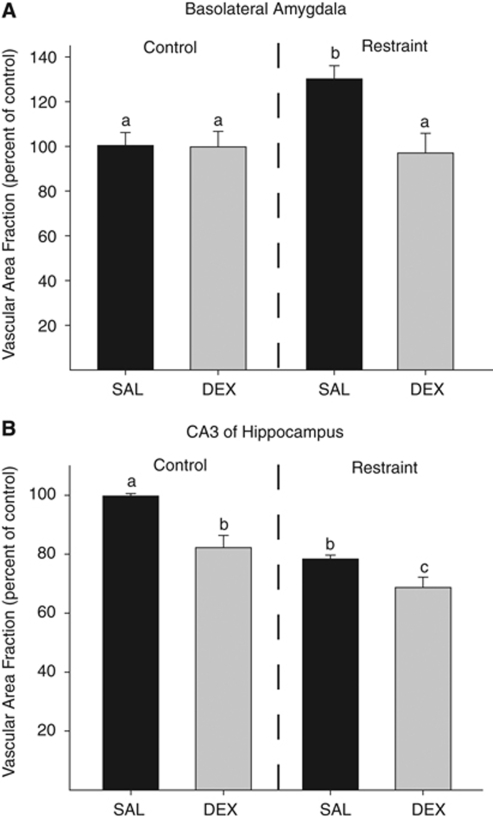
Figure 2.
(A) Chronic stress in adulthood increased vascularization in the basolateral amygdala (P<0.05 as compared with all conditions labeled with ‘a'). Dexamethasone in utero buffered against the chronic stress-induced change in vascularization in the amygdala such that there was no difference among DEX+STRESS and the control conditions (P>0.05), but the SAL+STRESS group had more area occupied by vasculature in the amygdala than those rats in the DEX+STRESS group (P<0.05). (B) Rats exposed to prenatal DEX have a reduced vascularization of the hippocampus as compared with rats prenatally exposed to saline (SAL; P<0.05). Chronic stress in adulthood also reduced hippocampal vascularization as compared with handled rats (SAL+CON; P<0.05). The combination of prenatal DEX+STRESS was additive such that vascularization was reduced as compared with SAL+CON, DEX+CON, and SAL+STRESS (P<0.05). Data are presented as mean±s.e.m.; n=6 for SAL+CON, SAL+STRESS, DEX+STRESS; n=7 for DEX+CON. DEX+CON, dexamethasone+adult control; SAL+CON, saline+adult control.