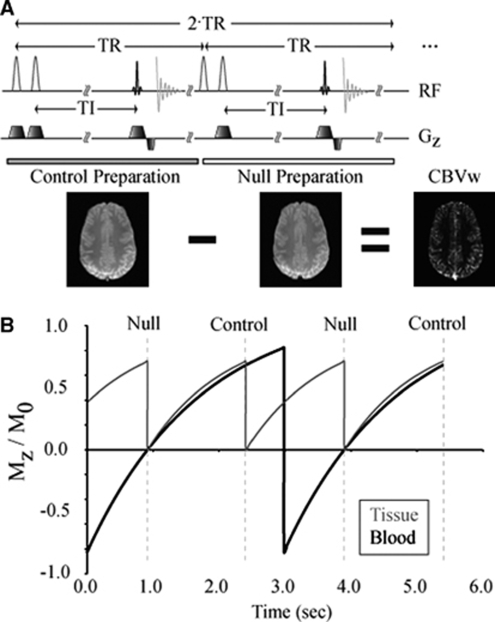
Figure 1.
(A) The inflow VASO with dynamic subtraction (iVASO-DS) pulse sequence. In the control preparation, two slice selective adiabatic inversion pulses are sequentially applied, followed by an inversion time (TI), and finally a 2D single-shot echo planar image gradient echo acquisition. In the control preparation, both blood and tissue magnetization are nonzero. After the control preparation, a null preparation is applied in which a nonselective adiabatic inversion is immediately followed by a slice-selective inversion (tissue ‘flip back'). The same TI is allowed, which corresponds to the time for the blood water magnetization to recover to zero. Control—null yields a CBVw map. (B) A snapshot in time of the tissue (gray) and inflowing blood (black) magnetization. This simulation has been performed for a representative TR/TI=1,492/914 ms. Note that tissue magnetization is only influenced by the readout excitation pulses, whereas the inflowing blood water magnetization is only influenced by an inversion pulse in alternate TRs.