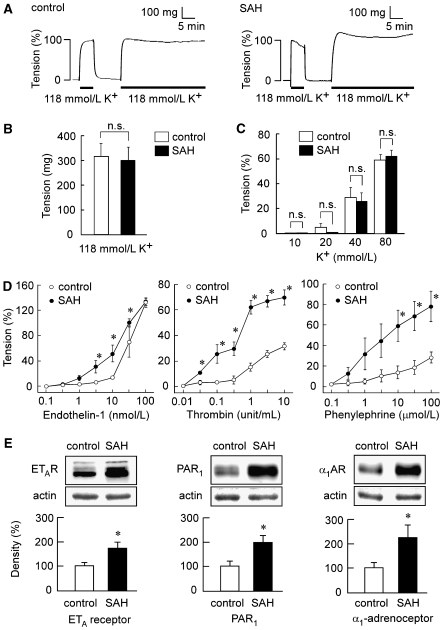
Figure 1.
Contractile responses of the rabbit basilar artery to high K+ depolarization, endothelin-1, thrombin, and phenylephrine and the expression of ETA receptor, proteinase-activated receptor 1 (PAR1), and α1-adrenoceptor in the controls and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). (A) Representative recordings showing the 118 mmol/L K+-induced contractions in the fura-2-unloaded basilar artery of controls and SAH. (B) The level of tension induced by 118 mmol/L K+ depolarization in the controls and SAH, as expressed in absolute value (n=5). (C) Concentration-dependent effect of high K+ depolarization on the tension development in the controls and SAH (n=5). (D) The concentration-response curves of the contraction induced by endotheliln-1, thrombin, and phenylephrine in the basilar artery of the controls and SAH (n=5 to 7). (E) Immunoblot analysis of the expression of ETA receptor, PAR1, and α1-adrenoceptor in the basilar artery of the controls and SAH (n=4 to 5). The level of tension obtained in normal physiological salt solution (PSS) and 118 mmol/L K+ PSS were assigned values of 0% and 100%, respectively. The level of expression observed in the controls was assigned to be 100%. The data represent the mean±s.e.m. n.s., not significantly different; *P<0.05 versus controls.