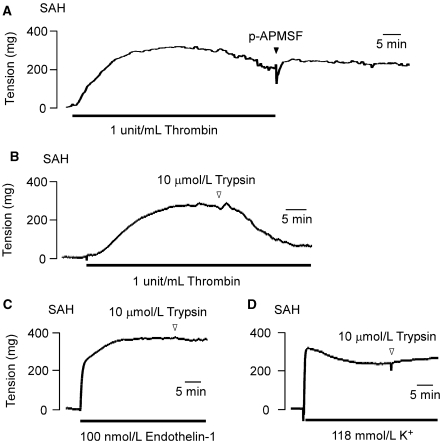
Figure 6.
The effects of trypsin on the sustained contractions induced by thrombin in the rabbit basilar artery with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Representative recordings of at least three independent experiments, showing the effect of the removal of thrombin on the subsequent time course of the thrombin-induced contraction (A) and the effect of 10 μmol/L trypsin on the contraction induced by 1 unit/mL thrombin (B), 100 nmol/L endothelin-1 (C), and 118 mmol/L K+ (D) in the fura-2-unloaded ring preparations of SAH. In panel (A), when thrombin was washed out, 10 μmol/L 4-amidinophenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride was added to the bathing buffer to ensure the complete inhibition of any residual thrombin activity.