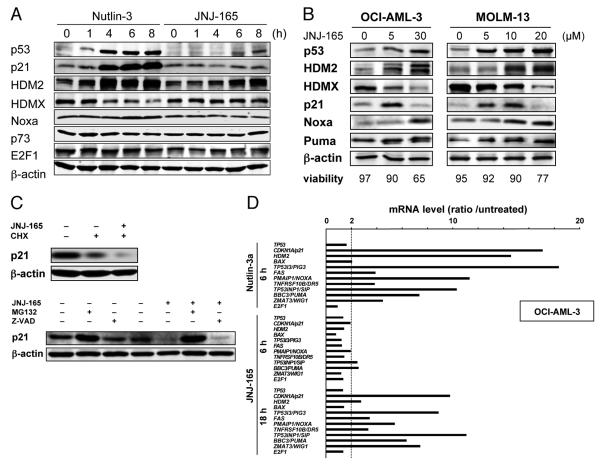
Figure 2. JNJ-26854165 induces p53 resulting in transcriptional activation of p53-regulated genes but enhances p21 degradation by proteasome activation.
(A) Protein expression in OCI-AML-3 cells, treated with 5 μM Nutlin-3 or 5 μM JNJ-26854165 for the indicated times. β-actin was used to confirm equal loading of proteins. (B) OCI-AML-3 and MOLM-13 cells were incubated with a range of concentrations of JNJ-26854165 for 18 hours. (C) OCI-AML-3 cells were preincubated for 1 hour with 70 μM cycloheximide, 10 μM MG132 or 100 μM Z-VAD-FMK, and p21 levels were determined after a 4-hour treatment with 10 μM JNJ-26854165. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (D) p53-target gene activation in response to 5 μM Nutlin-3 and 10 μM JNJ-26854165 in OCI-AML-3 cells. Ratios represent Nutlin-3 or JNJ-26854165 values divided by untreated values. Each value represents the mean of two independent experiments (each assayed in duplicate). JNJ-26854165 treatment did not alter p53 mRNA levels, suggesting that JNJ-26854165 has little effect on p53 synthesis.