Figure 7.
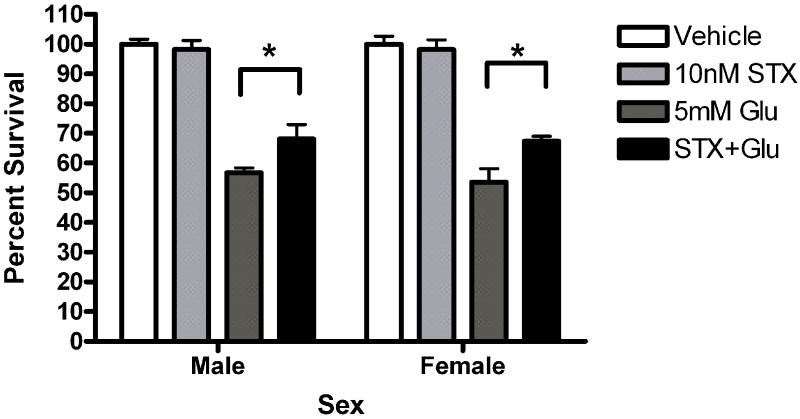
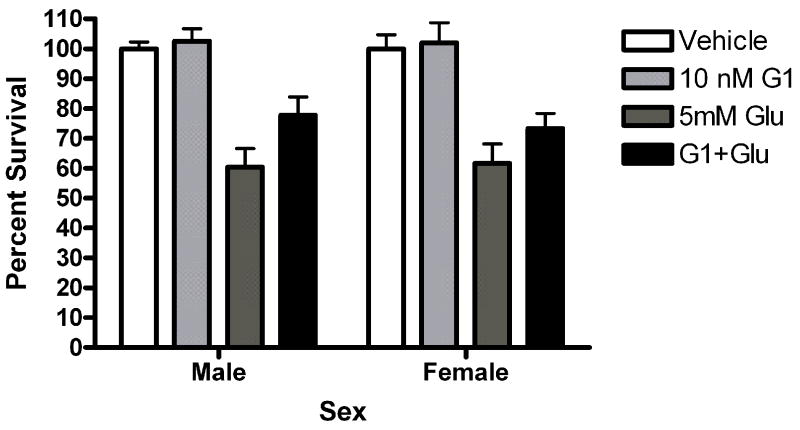
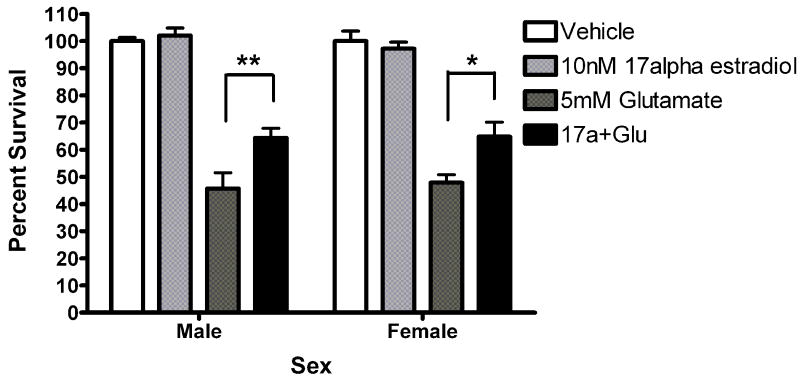
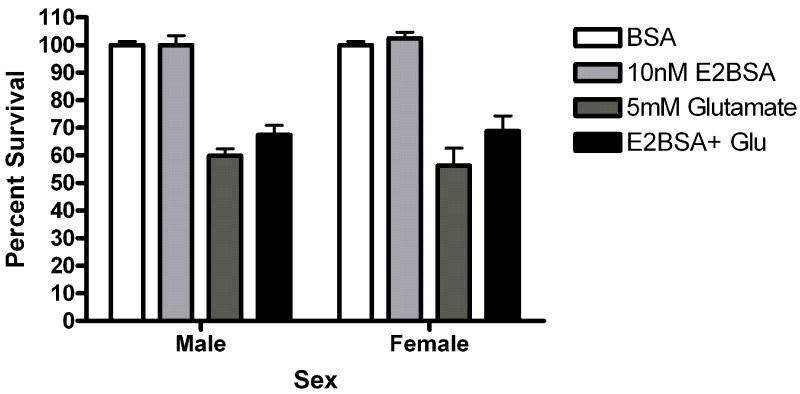
(A) STX and 17α-estradiol protect male and female neurons. Neurons were exposed to 10 nM STX for 5 minutes prior to a 5 minute exposure to 5mM glutamate. STX protected both male (*Bonferroni post hoc t (glutamate vs. STX+ glutamate) =2.557,p<0.05, n=3) and female (*Bonferroni post hoc t (glutamate vs. STX+ glutamate) =3.076,p<0.05, n=3) neurons from glutamate toxicity.(7b) Neurons were exposed to 10nM of the non-steroidal GPR30 agonist G1for 5 minutes prior to exposure to glutamate. G1 was not neuroprotective (n=3) (7c) Neurons were exposed to 10 nM of 17α estradiol for 5 minutes prior to a 5 minute exposure to 5mM glutamate. 17α- estradiol is neuroprotective in male (post hoc tglutamate vs 17α- estradiol+glutamate=3.507,p<0.01) and female (post hoc tglutamate vs 17α-estradiol+glutamate=3.18, p<0.05) neurons (n=3). (7d) Neurons pre-exposed to 10nM bovine serum albumin conjugated estradiol for 5 minutes were not protected from glutamate toxicity (n=3).