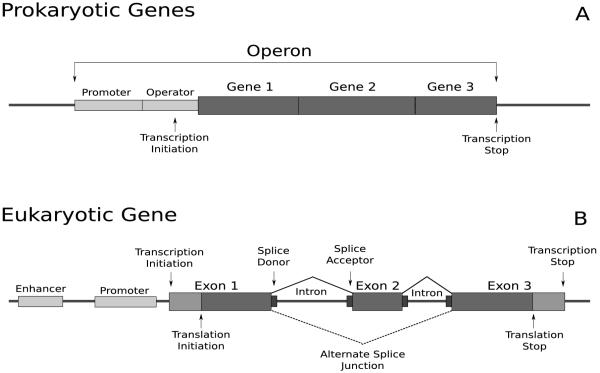
Figure 1.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene structures. A: Prokaryotic genes may be arranged in an operon, sharing the same promoter. B: A eukaryotic gene contains protein-coding regions called exons, separated by non-protein-coding regions called introns. Once transcribed, the introns are spliced out. An alternate splice junction is shown using a dotted line.