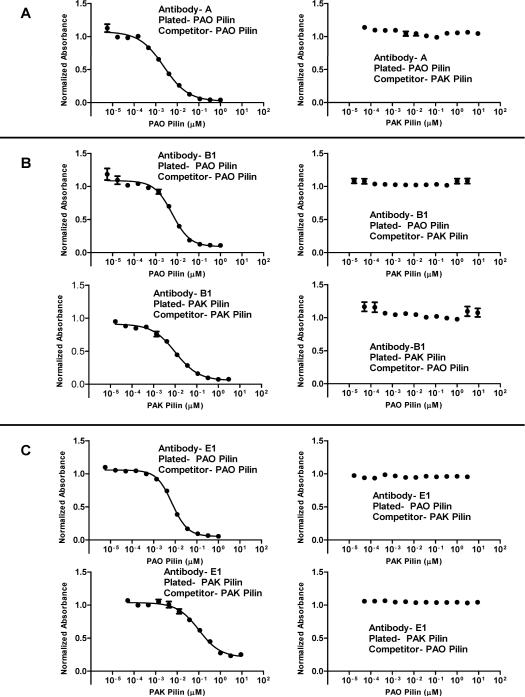
Figure 4.
Competitive ELISAs using three representative groups of antibodies; A, PAO pilin specific antibodies, B1, PAK/PAO cross-reactive antibodies, and E1, PAK/PAO cross-reactive antibodies. The antibodies were purified as described in the methods. Panel A shows antibody A in a PAO-PAO pilin and PAO-PAK pilin competition ELISA. The results, coupled with indirect ELISA results, show that antibody A is PAO pilin specific. Panel B shows antibody B1 in PAO-PAO pilin, PAO-PAK pilin, PAK-PAK pilin, and PAK-PAO pilin competition ELISAs. As shown, PAK pilin cannot compete B1 antibodies off PAO pilin and vice versa; PAO pilin cannot compete B1 antibodies off PAK pilin. This indicates that there are at least two distinct antibodies in B1 with different epitopes, one PAO pilin specific and one PAK pilin specific. Panel C shows antibody E1 in PAO-PAO pilin, PAO-PAK pilin, PAK-PAK pilin, and PAK-PAO pilin competition ELISAs. The results are similar to the B1 antibody results and indicate that there are at least two distinct antibodies in E1, one PAO pilin specific and one PAK pilin specific. Antibodies are designated by letter based on the peptide immunogens shown in Figure 2.