Fig. 1.
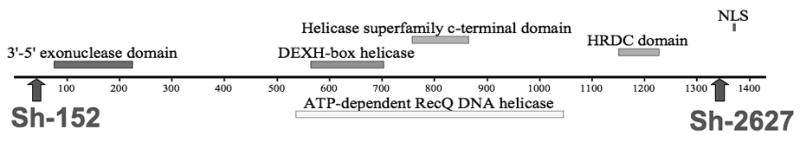
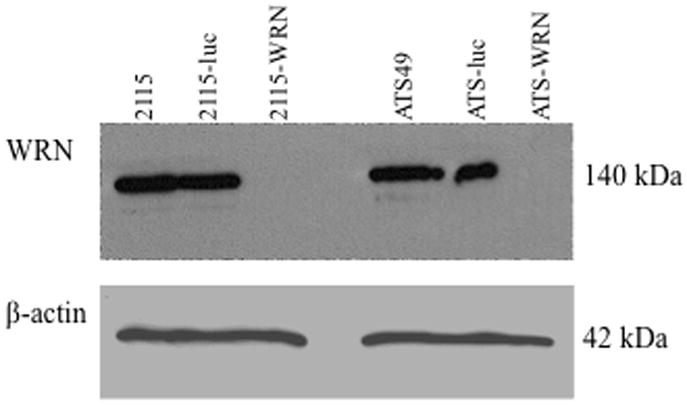
shRNA knock-down of CHO WRN at the protein level. (A) Diagram of WRN protein with conserved protein domains identified by boxes above and below the line. The locations of the two shRNA sequences are indicated by arrows. Sh-152 was used in the pSilencer-puro vector and was transfected into CHO cell lines first. Sh-2627 was cloned into the hygromycin version of the vector. Maximum knock-down of CHO WRN was achieved by sequential transfection of both shRNA vectors. (B) Western blot demonstrating knock-down in parental, control and WRN deficient cell lines. WRN was depleted in two CHO cell lines: GS21-15 and ATS-49tg to generate lines 2115-WRN and ATS-WRN respectively. A shRNA to luciferase was transfected into the same two CHO cell lines to generate non-specific shRNA control cell lines 2115-luc and ATS-luc.. βactin served as a loading control antibody.
