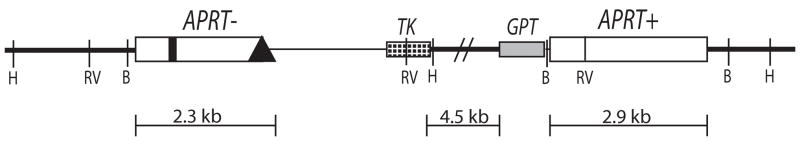
Fig. 3.
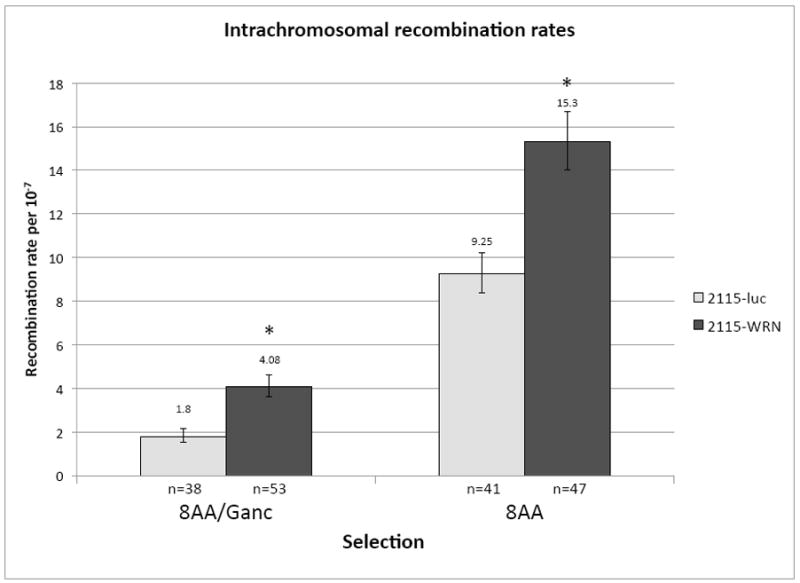
Intrachromosomal recombination assay. (A) Diagram of endogenous recombination substrate fixed at the endogenous APRT locus in GS21-15-derived CHO cell lines. The upstream copy of APRT is inactivated by a transversion mutation in exon 2 abolishing an EcoRV restriction site (thick black vertical line) and a deletion of the terminal portion of exon 5 (black diamond). The downstream copy of APRT is wild-type and retains the EcoRV restriction site (RV). Two selectable markers lie between the APRT copies: TK (checked box) and GPT (grey box). Sizes of regions are shown below. Chromosomal sequence is denoted by thick lines while the thin line between the upstream APRT and TK indicates sequence retained from the targeting plasmid used to generate this construct. Various restriction sites used to distinguish recombination products are also indicated (H: HindIII, B: BamHI, RV: EcoRV). (B) Recombination rates using intrachromosomal recombination assay for control (light bars) and WRN deficient (dark bars) GS21-15-derived cell lines. Recombination rates were calculated using fluctuation analysis and the MSS-MLE method. Error bars indicate 95% confidence limits. 8AA/Ganc was used to select for APRT−/TK− and 8AA to select for APRT− recombinants. The number of independent populations used is indicated below each bar. * indicates p<0.05.