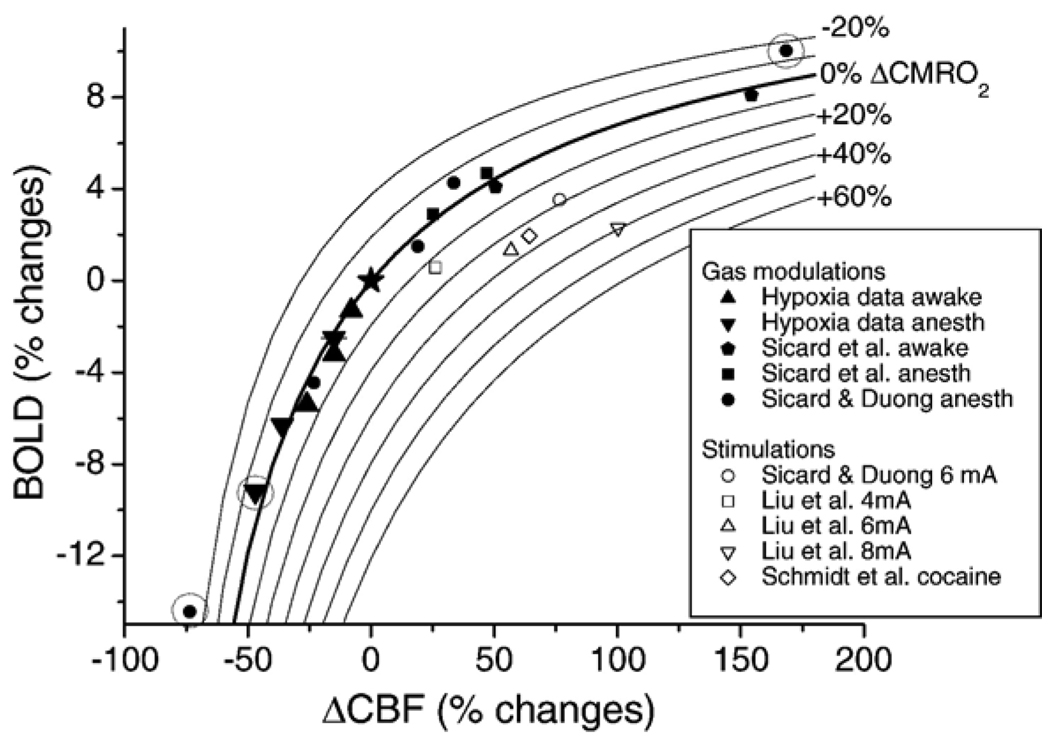
Fig. 6.
Iso-CMRO2 contour lines from −20% to 60% in steps of 10% are overlaid on the plot of BOLD versus CBF percent changes under different physiological modulations and functional stimulations. CMRO2 contour lines were calculated using M=0.16, α of 0.4, and β of 1.2. The open data points were functional (forepaw or cocaine stimuli) stimulations and the solid data points were physiological modulations (normal conditions, hypercapnia, hyperoxia or hypoxia). ▲ and ▼ are awake and anesthetized hypoxia data obtained from this study; ⬟ and ■ are CO2 challenges data under awake and anesthetized conditions, respectively, obtained from (Sicard et al., 2003); ● and ○ are CO2 challenges and 6 mA forepaw stimulation data, respectively, obtained from (Sicard and Duong, 2005);□, △, and ▽ are 4, 6, and 8 mA forepaw stimulation data, respectively, obtained from Liu et al. (2004); ◊ is cocaine data (1 mg/kg) from Schmidt et al. (2006). Three data points that are encircled show deviation from the 0% CMRO2 iso-contour line: ▼ at ~50% ΔCBF and ● at ~70% ΔCBF were 9% O2 hypoxia under anesthesia, and ● at 170% ΔCBF was 10% CO2 hypercapnia under anesthesia. ★ indicates the point of origin.