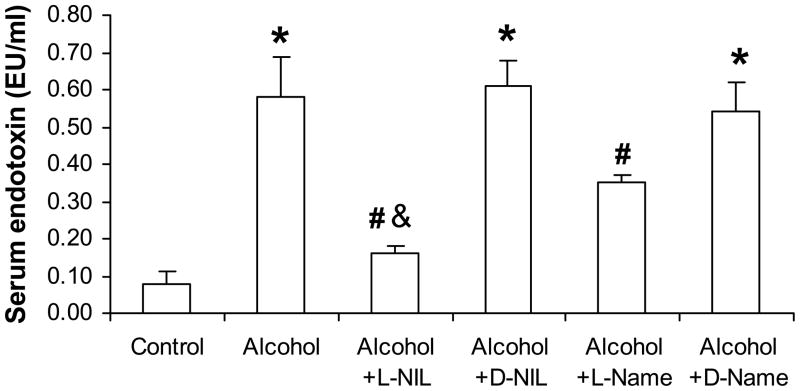
Fig. 5.
iNOS inhibitors prevented EtOH-induced increases in serum endotoxin. Serum endotoxin was determined for control and alcohol-fed rats at 10 weeks after alcohol feeding as described in Methods. Serum endotoxin levels were significantly higher in alcohol-fed rats. iNOS inhibitors (L-NIL or L-NAME) prevented EtOH-induced increases in endotoxin levels. Data are expressed as mean endotoxin Units (EU) per ml serum ± S.E. for N=6 rats for each group. The difference between groups was analyzed by ANOVA, *: p<0.05 compared to the control group, #: p<0.05 compared to alcohol-fed rats (10 weeks), &: p<0.05 compared to alcohol + L-NAME group.