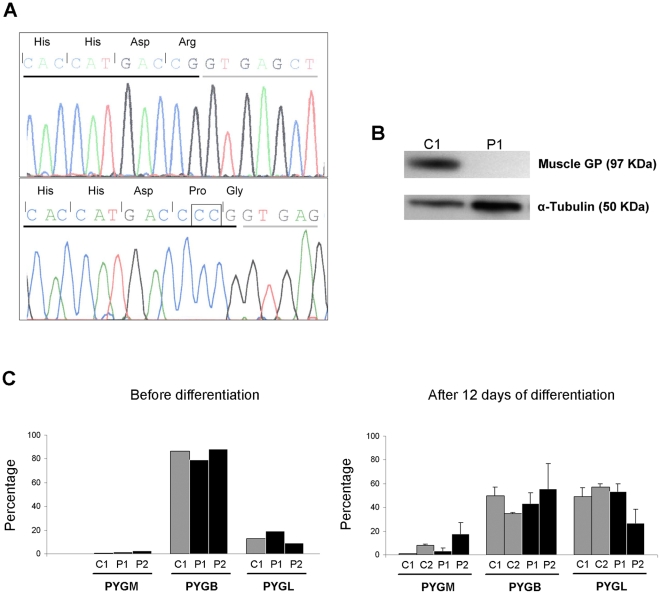
Figure 1. Molecular effects of c.2310_2311dupCC mutation and GP isoforms expression in muscle cells.
(A) Electropherogram of PYGM exon 18 in control C1 (top) and patient P1 (bottom). The square shows the c.2310_2311dupCC mutation. Exonic nucleotides are underlined in black; intronic nucleotides are underlined in grey. Encoded amino acids are indicated (including wild type Arg, and mutant Gly, encoded by codons formed in an exon-exon junction). (B) Immunoblotting showing muscle GP and α-tubulin bands in muscle biopsy homogenates from control C1 and patient P1. (C) Relative contribution of each gene (PYGM, PYGB and PYGL), to the total amount of GP mRNA in undifferentiated and 12 day differentiated cultured muscle cells. Bars represent the result of a single experiment for undifferentiated cells, or mean ± SD of two independent experiments for 12 days differentiated cells. Percentages were calculated as [PYG(x) mRNA x 100/(PYGB mRNA + PYGL mRNA + PYGM mRNA)], using values normalized for the PPIA mRNA. In C1 and C2 skeletal muscle (not shown), PYGB mRNA and PYGL mRNA were negligible (<0.5%).