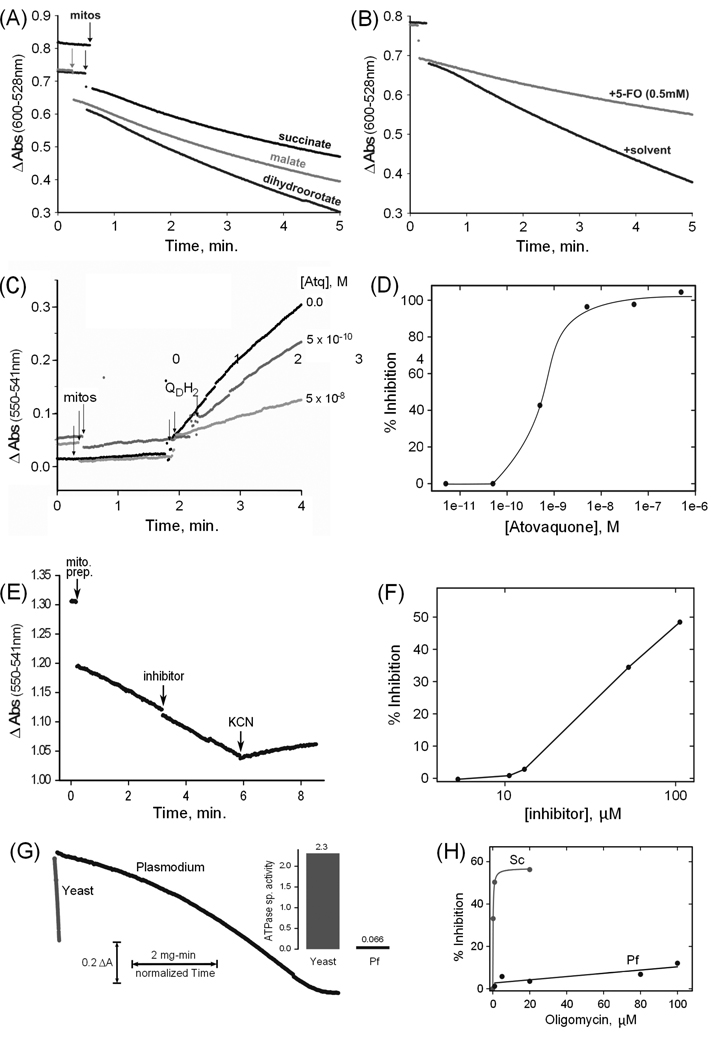
Fig. 2. Spectrophotometric assays of mitochondrial enzyme activities.
(A) Example assays of dihydroorotate, malate and succinate QD/2,6-Dichloroindophenol reductase activities of a P. falciparum mitochondrial preparation (B) Example dihydroorotate reductase assays plus and minus the inhibitor 5-fluoroorotate (5-FO). (C) Time courses of ubiquinone cytochrome c reductase assays in the absence and in the presence of two concentrations of atovaquone. The points of addition of aliquots of mitochondrial preparation (mitos) and of substrate (QDH2) are indicated. (D) Profile of the inhibition by atovaquone of the ubiquinone cytochrome c reductase activity of a mitochondrial preparation. (E) Time course of a cytochrome c oxidase assay. The points of addition of an aliquot of mitochondrial preparation (mito. prep.), of the potential inhibitor 2,5-bis(4-amidinophenyl)furan (inhibitor; 13 µM final), and of potassium cyanide (KCN; 2 mM final) are indicated. Cytochrome c is present from the beginning of the assay. (F) Profile of the inhibition by 2,5-bis(4-amidinophenyl)furan of the cytochrome c oxidase activity of a mitochondrial preparation. (G) Example ATPase assay time course curves for an aliquot of P. falciparum mitochondrial preparation compared to one of yeast mitochondria, normalized to mitochondrial protein to allow visualization of the rate difference. The inset to the right of the curves displays the corresponding ATPase specific activities in µmol ATP/min/mg protein (Pf = P. falciparum). (H) Profile of oligomycin inhibition of the ATPase activities of a P. falciparum preparation (Pf) and a yeast (Sc) mitochondrial preparation. Succinate, malate, and dihydroorotate quinone reductase activities were measured essentially as described [14], using 10 mM succinate, 10 mM D,L-malate, or 2 mM dihydroorotate. Cytochrome c reductase activity was assayed by a modification of the method of Trumpower and Edwards [15], using 100 µM QDH2 and 100 µM horse heart cytochrome c (Sigma-Aldrich). Cytochrome c oxidase activity was determined by measuring the oxidation of 100 µM reduced horse heart cytochrome c. The diamidine compound 2,5-bis(4-amidinophenyl)furan was provided by Steven Meshnick, University of North Carolina. ATPase activity was determined by a coupled assay modified from Pullman et al [16], using 3 mM phosphoenolpyruvate, 0.3 mM NADH, 4 units lactate dehydrogenase (Sigma), 4 units pyruvate kinase (Sigma) and 1 mM ATP, and including inhibitors of possible contaminating activities. The assays described above were all recorded with a modified SLM-AMINCO DW2C dual wavelength spectrophotometer (On-Line Instrument Systems, Inc., Bogart, GA, USA) in dual mode (600 nm – 528 nm for 2,6-Dichloroindophenol reduction, 550 nm – 541 nm for cytochrome c oxidation/reduction, and 341 nm – 401 nm for NADH oxidation). Yeast mitochondria were prepared as described [17] and stored in aliquots at −80 °C.