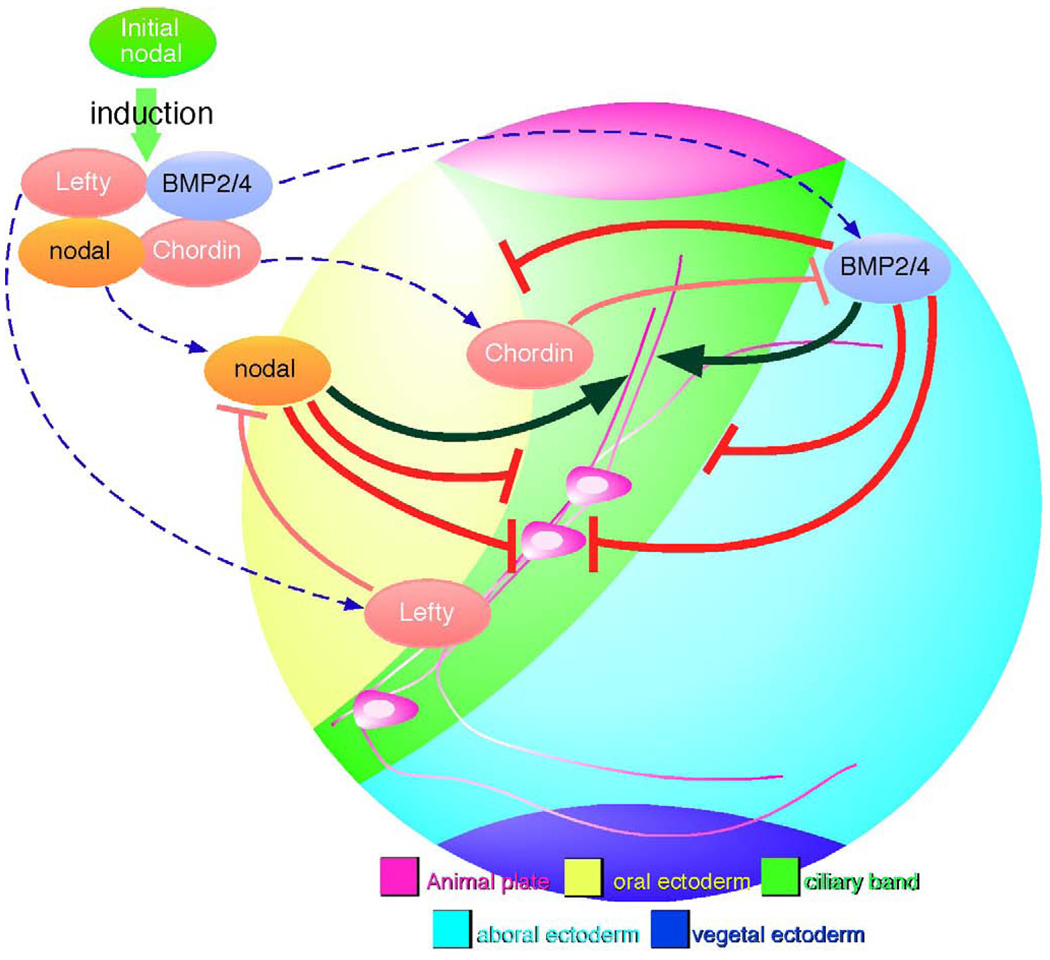
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram for the signaling pathways regulating ciliary band formation and the differentiation of ciliary band-associated neurons. Nodal expression in the oral ectoderm initiates expression of factors that antagonize or modify Nodal and BMP2/4 signals. Lefty and Chordin exclude TGFβ signals from the presumptive ciliary band (thin red barheads). Localized Nodal signaling positions the oral margin of the ciliary band and BMP signaling through Alk3/6 narrows the width of the ciliary band (barheads to ciliary band margins). This model proposes that an indirect effect of TGFβ signaling is to provide the appropriate environment for neural differentiation. Exclusion of BMP and Nodal from the ciliary band ectoderm is required for the differentiation of neurons and the outgrowth and bundling of axons. Oral ectoderm cannot support these events and aboral ectoderm only promotes growth of unbundled neurites. Thus, Nodal and BMP2/4 block development of most, if not all, ciliary band neurons (barheads to neural cell body), yet the correct patterning of these cells within the ciliary band depends on the presence of both of these signals (black arrowheads to axons).