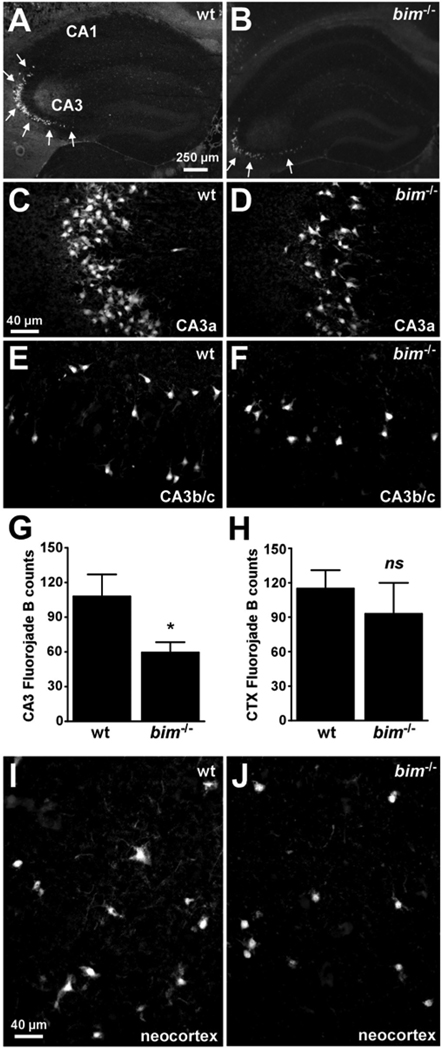
Figure 5. Hippocampal but not neoortical seizure damage is reduced in bim−/− mice.
(A, B) Representative photomicrographs (4× lens) of Fluoro-Jade B staining within the ipsilateral hippocampus 72 h after status epilepticus in wild-type (wt) and bim−/− mice. Note the reduction in numbers of damaged/dying cells within CA3 in bim−/− mice compared to wild-type animals. (C–F) Representative photomicrographs (40× lens) of Fluoro-Jade B staining within the ipsilateral hippocampal CA3a and CA3b/c regions 72 h after status epilepticus in wild-type and bim−/− mice. Note, the reduced numbers of Fluoro-Jade B positive cells in bim−/− mice compared to wild-type animals. (G, H) Graphs quantifying numbers of Fluoro-Jade B stained cells in the hippocampal CA3 and the neocortex for each genotype of mice. Data are derived from n = 6–10 per group. *p < 0.05. ns, not significant. (I, J) Representative photomicrographs (4× lens) of Fluoro-Jade B staining within the ipsilateral neocortex 72 h after status epilepticus in wild-type and bim−/− mice.