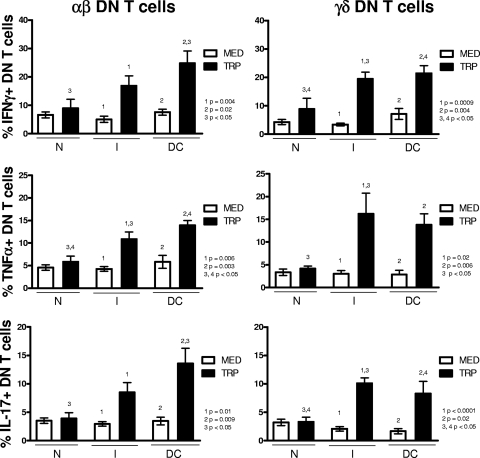
FIG. 2.
T. cruzi activation of peripheral blood cells induces specific inflammatory cytokine production by αβ and γδ DN (CD4− CD8−) T cells from both indeterminate and dilated cardiac chagasic patients. Whole blood cells from noninfected controls (N), indeterminate chagasic patients (I), and dilated cardiac chagasic patients (DC) were incubated overnight with either medium alone (MED) or with live T. cruzi parasites (TRP) and then analyzed for the frequency of αβ or γδ DN T cells producing specific cytokines using flow cytometry, as described in Materials and Methods. The data represent the average for each group ± standard deviations. The numbers of individuals in each group were as follows: N, seven; I, seven; and DC, five. The top panel shows the average percentage of IFN-γ-producing cells within αβ or γδ DN T cells from individual cultures without (MED) or with (TRP) stimulus. The middle panel shows the same for TNF-α-producing cells within αβ or γδ DN T cells, and the bottom panel shows the values for IL-17-producing cells within αβ or γδ DN T cells. Statistical significance is indicated in each graph, with differences between groups indicated by common numbers. Comparisons between groups were performed using a Tukey-Kramer comparison of all pairs, and comparisons within groups (MED versus TRP) were performed using a paired t test, as described in Materials and Methods. All patients were meticulously classified based on clinical criteria, as described in Materials and Methods.