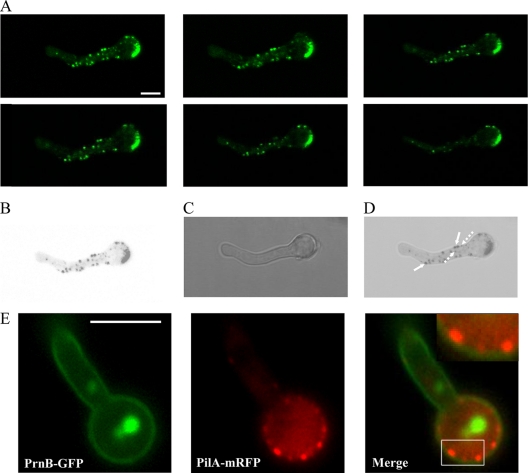
Fig. 3.
(A) Confocal z-stack sections showing PilA-GFP in a wild-type strain. The strain was grown in the presence of 5 mM urea and 1% (wt/vol) glucose as the sole nitrogen and carbon sources, respectively, for 16 h at 25°C. (B to D) Inverted black and white fluorescence of the first z-stack section merged to the corresponding DIC. Bar, 5 μm (A to D). Note that PilA spots are not uniform in size and are not restricted at the periphery of mycelia. The largest PilA eisosomes (filled arrows in panel D) are localized at the periphery, while the smaller ones are at both the interior and the periphery (dashed arrows). (E) Subcellular localization of PilA and PrnB proteins in mycelia. Representative pictures from laser scanning confocal microscopy of strains expressing both PilA-mGFP and PrnB-GFP molecules in young mycelia (12 h) are shown. The upper right inset in the Merge panel shows a magnification of the boxed region. Strains were grown in the presence of 5 mM urea and 1% (wt/vol) glucose as the sole nitrogen and carbon sources, respectively, at 25°C. To induce prnB gene expression, 20 mM l-proline was added during the last 2 h of growth (45). Bar, 5 μm.